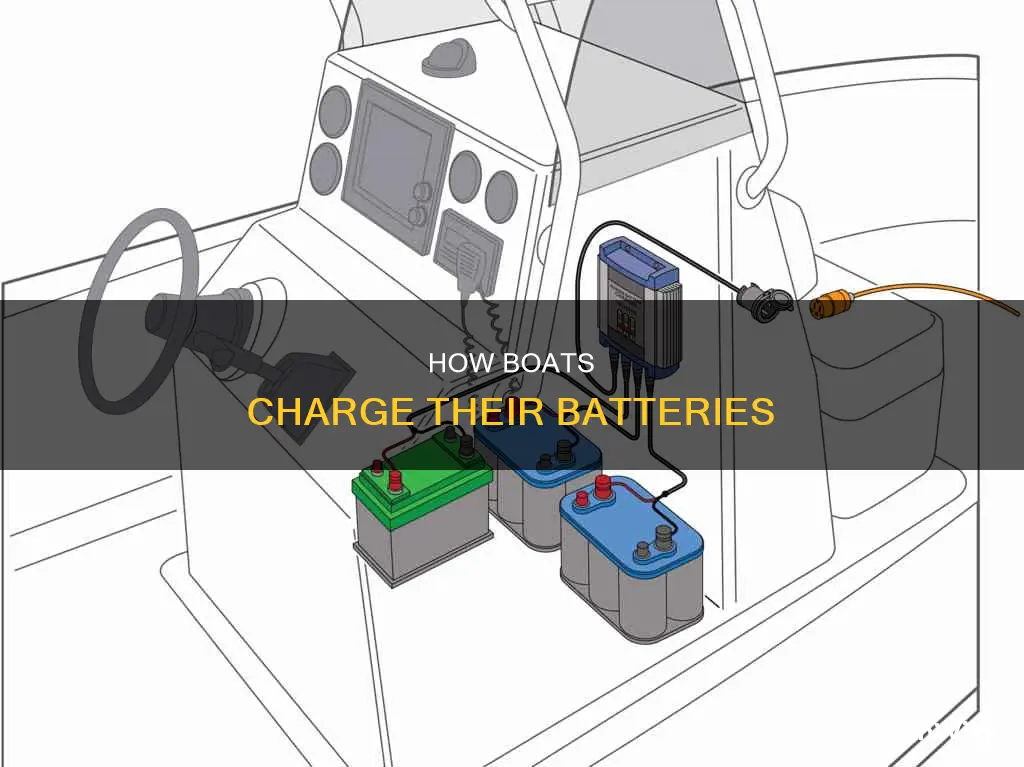
Marine batteries are an essential component of a boat's electrical system, providing the power needed to start the engine and operate electronics and accessories. Similar to car batteries, boat batteries require proper maintenance to ensure they don't suddenly die when taken out on the water. A boat typically charges its battery through an alternator or a similar charging system that sends a charge to the battery as the motor runs. While a boat's battery usually requires minimal attention, it's important to perform occasional check-ups on the electrical and mechanical systems to ensure optimal performance.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| How does a boat charge its battery? | Via an alternator, or similar charging system, that is located on the boat. |
| When does a boat charge its battery? | As the motor runs, it sends a charge, via the alternator or similar device, to the battery. |
| How often should a boat battery be charged? | It is recommended to give the entire electrical system on a boat a check-up once or twice per year. |
| How long does it take to charge a boat battery? | If everything is working correctly, the motor will charge a boat battery via the alternator. If a marine battery charger is used, it will usually take between 4-6 hours depending on the state of its depletion. |
| How to check boat battery charge level | Use a simple battery tester to check the battery charge level. |
| How to charge a boat battery | Always use a smart charger to restore a full charge to your boat battery. |
| How to maintain a boat battery | Clean any dirt or grime on the battery casing. Ensure the battery terminals/posts are corrosion-free. Ensure the electrolyte levels on the battery are at optimal levels. Make sure the battery has a full charge. |
| Types of boat batteries | Cranking Battery, Deep-Cycle Battery, Dual-Purpose Battery |
What You'll Learn

Boat battery charging problems and solutions
Problem: Dead Battery
Solution:
- Check the battery's voltage regularly and recharge when necessary.
- Ensure the battery is clean and dry.
- Store the battery in a cool, dry location.
- Use a maintenance-type battery charger to keep the battery charged when the boat is not in use.
- Consider upgrading to a lithium-ion battery, which has a longer life cycle and can be recharged faster.
Problem: Battery Won't Hold Charge
Solution:
- Regularly charge your battery to prevent sulfation, which occurs when lead sulfate crystals build up and reduce battery capacity.
- Check for a parasitic load, where a device is drawing power even when the boat is off.
- If your battery is several years old, it may need replacing.
Problem: Poor Charging System
Solution:
- Upgrade to a smart charger, which optimizes the charging process and prevents overcharging.
- Ensure the battery charger is compatible with your battery's voltage and amperage requirements.
- Install a voltage sensitive relay (VSR) to automatically switch between batteries when needed.
Problem: High-Watt Stereo Systems and DC-Powered Refrigerators Draining Battery
Solution:
- Consider stepping up to a higher output alternator to compensate for the high power demand of these appliances.
- Dedicate one battery for starting and another for house loads.
Problem: Faulty Installation or Poor Maintenance
Solution:
- Ensure the battery is kept clean and dry, with no dirt or corrosion buildup on the terminals.
- Check that the battery is not sitting on a wet or damp surface, as this can cause rapid discharge.
- Relocate the battery to a more accessible location if it is difficult to reach or service.
- Use high-quality battery cables and connectors to avoid high resistance connections.
Boat Shoes: Stinkers or Sweet-Smelling Sailors?
You may want to see also

How to test if your battery is charging
To test if your boat battery is charging, you will need a voltmeter or multimeter.
First, locate the positive and negative terminals on your battery. These are marked on the battery. The positive terminal will be red, and the negative terminal will be black.
Next, set the voltmeter or multimeter to the DC setting. This stands for direct current, which is the type of current that batteries use.
Now, touch the positive and negative probes to the positive and negative battery terminals respectively. The red probe is positive, and the black probe is negative.
If you have connected the probes correctly, the meter will produce a reading within a few seconds.
A fully-charged battery should have a reading of 12.5V to 12.6V. If the reading is below 12.2V, the battery needs to be recharged. If it is below 12V, the battery is dead.
You can also test the battery while the engine is running. With the engine idling, check the voltage. Then, advance the throttle to about 1200 RPM. As the RPM increases, the voltage should also increase. The voltage should peak at around 14 VDC.
Boat Slips in Southwest Florida: A Rare Find?
You may want to see also

How to wire and use a battery selector switch
A boat's electrical system is powered by a marine battery, which provides the necessary power to start the engine, run electronics, and keep everything functioning while the boat is in use. Marine batteries are designed to handle the unique challenges of the marine environment, such as moisture, water, and condensation.
Now, let's get into the details of how to wire and use a battery selector switch.
Wiring a Battery Selector Switch:
- First, identify the type of battery selector switch you have. It should have three terminals or posts: one for battery 1, one for battery 2, and a common or "C" post.
- Connect the positive terminal of battery 1 to terminal 1 on the switch.
- Connect the positive terminal of battery 2 to terminal 2 on the switch.
- The common or "C" post is where you will connect the starter/accessory circuits, which are typically connected to the positive post of battery 1.
- Ensure that your switch is a ""make before break" type, which means it makes the new connection before breaking the existing one. This is important for safely switching between batteries while the engine is running.
- For the negative terminals, you have two options: tie the ground from battery 2 to the ground of battery 1, or run a separate ground wire from battery 2 to the engine block or the same ground location as battery 1.
Using a Battery Selector Switch:
- When starting the engine, you can use either battery 1 or battery 2 by selecting the corresponding position on the switch.
- To charge both batteries while the engine is running, select the "Both" position on the switch. This is safe to do as long as your switch is a "make before break" type.
- When sitting in the water, you can select battery 1 to prevent drain and conserve power.
- If battery 1 runs low or you need additional power, you can switch to battery 2.
- Always remember to switch off the engine before turning the selector switch to the "Off" position to avoid damaging the alternator diodes.
By following these wiring and usage instructions, you can effectively manage your boat's power supply and ensure that you have sufficient power for your engine and electronics during your boating trips.
The Fateful Voyage of the SS Minnow
You may want to see also

How to maintain and extend the life of your marine battery
Maintaining your marine battery is essential to ensuring your boat runs smoothly. Here are some tips to help extend the life of your marine battery:
Keep the Battery at the Right Temperature
Marine batteries are durable, but they are sensitive to extreme temperature changes. High temperatures can shorten the lifespan of your battery, and when a marine battery gets too hot, it may expand and use up its energy faster as it loses electrolytes too quickly. On the other hand, when a battery gets too cold, it has to work harder to power the boat. Therefore, it is recommended to keep your marine battery in a moderate climate. If necessary, remove the battery and store it in a temperature-controlled environment when your boat is docked during extreme weather conditions.
Recharge Your Marine Battery Regularly
It is important to recharge your marine battery immediately after use to prolong its life. Allowing the battery to remain partially charged can lead to lead sulfate deposits, making it harder for the battery to generate an electrical current. Similarly, rapid charging at high voltage for a short period can also increase sulfate deposits, reducing the battery's life. Thus, it is best to plan to recharge the battery fully after each use, following the manufacturer's instructions.
Keep the Battery Clean
It is crucial to maintain a clean marine battery to ensure optimal performance. Allowing battery acid to accumulate on the terminals, connectors, and other components can hinder its ability to start up or charge. To clean the battery terminals, disconnect them and apply a paste made from baking soda and water with a toothbrush. Alternatively, you can use a wire brush to scrub away any corrosion or debris. After cleaning, protect the terminals by applying petroleum jelly before reconnecting them.
Fill the Battery with Distilled Water
Most marine batteries require regular refilling with distilled water to function properly. Distilled water can be purchased at most stores, and by maintaining the water level as per the manufacturer's recommendations, you can help ensure the longevity of your battery.
Check Battery Terminal Connections
Frequently inspect the battery terminal connections to ensure they are tight, clean, and free from corrosion. Look out for any cracks, bulges, or leaks, and address any issues promptly. Corrosion around the terminals can impede the battery's functionality, so regular cleaning with a baking soda and water solution is essential.
Protect the Battery from Vibration
Vibration can be detrimental to your marine battery. Ensure the battery is securely mounted and stored in a battery box or tray to minimize movement during rough waters. Additionally, consider using a rigid bracket or a locking strap to hold the battery in place.
Use a Maintenance-Type Battery Charger for Infrequent Use
If you don't use your boat often, it is advisable to use a maintenance-type battery charger to keep the battery fully charged between outings. Before off-season storage, remember to completely charge the batteries and then disconnect the terminals to prevent any power draw. If possible, keep the batteries on a battery maintainer/charger during the off-season to maintain them in optimal condition.
By following these maintenance tips, you can extend the life of your marine battery, ensuring reliable and efficient performance from your boat.
Transform Paddle Boats: Install Trolling Motors for Easy Maneuvering
You may want to see also

How to charge a boat battery
Choose the Right Charger
There are many different types of boat batteries, so you'll find a wide range of battery chargers on the market. The best charger for your boat battery will be designed specifically for its chemistry and voltage. If you have more than one battery on board, ensure the charger can accommodate both.
Boat battery chargers fall into one of two categories: onboard and portable. Onboard chargers are already connected to the battery system, so all you need to do is hook them up to a standard 120-volt outlet. Portable chargers, on the other hand, are known for their portability and lower price point.
Select the Right Time
Charging a boat battery requires certain conditions. The optimal charging temperature for ionic lithium batteries is above freezing, but you can charge them at temperatures as low as -131°F without causing damage.
Clean the Battery Terminals
Grimy battery terminals can disrupt the charging process, so be sure to clean them before you begin.
Connect the Battery Charger
To connect the charger:
- Connect the red (positive) cable to the red terminal.
- Connect the black (negative) cable to the black terminal.
- Plug in the charger and turn it on.
If you're using a smart charger, you can leave it to automatically stop charging when it's finished. Ionic lithium chargers often have Bluetooth capabilities, making it easy to monitor their progress. If you're using a lead-acid charger, you'll need to set a timer and manually disconnect it once the battery is fully charged.
Disconnect the Charger
Once the battery is fully charged, unplug the charger and remove the cables, first detaching the black cable, followed by the red one.
Additional Tips:
- It will take about four to six hours for a marine battery to charge from 0% to 80% using a charger designed specifically for it.
- You can charge your boat's battery while it's in the water using a portable charger.
- Expect your marine battery to hold its charge for about six months.
- The cost of a marine battery charger depends on its size and power requirements, but prices typically range from $100 to $500.
- Boat batteries last three to four years, and sometimes up to six years under the right conditions.
- The replacement battery cost will be between $100 and $500.
- Always use a charger designed for marine batteries. Overcharging or undercharging can reduce the battery's lifespan.
- Different types of batteries require different charging voltages. For example, a 12-volt deep-cycle battery should be charged to around 14.4-14.8 volts.
- Consider using a trickle charger to maintain battery health when your boat is not in use.
- If you use your boat infrequently, use a maintenance-type battery charger to keep the battery fully charged between outings.
- Before off-season storage, fully charge the batteries, then disconnect the terminals. If you have access to power at your storage site, keep the batteries on a battery maintainer/charger. Otherwise, remove the batteries and store them where they can be connected to a maintenance charger.
- Store your battery in a cool location to prevent overheating or freezing.
- Check the battery's voltage regularly during storage and recharge as necessary to prevent deep discharge.
- Regularly check the battery terminal connections to ensure they are snug and free from corrosion.
- Clean the terminals using a mixture of baking soda and water.
- Keep the battery cool and out of direct sunlight.
- Secure the battery with a battery box or tray to prevent damage from vibrations.
- Install a cover or "boot" over the top of the positive battery terminal to prevent sparks and arcing.
- If you're storing your boat during the off-season, always fully charge your battery before storing it in a climate-controlled environment.
- Attach the battery to a trickle charger to keep it charged throughout the winter, or check it monthly and recharge as needed.
Boat Insurance and Theft: Are You Covered by Progressive?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A boat charges its battery via an alternator or similar charging system. As the motor runs, it sends a charge to the battery via the alternator.
It is recommended to check the battery charge level every now and then to quickly identify any possible charging difficulties. If everything is working correctly, the motor will charge the battery via the alternator. This is an ongoing process that is imperceptible to the boat operator.
If everything is working correctly, it will usually take between 4-6 hours to charge a boat battery, depending on the state of its depletion.
Common signs that it's time for a replacement include slow cranking, swelling or leaking, and reduced capacity. Marine batteries typically last 3-5 years, but this depends on use and maintenance.







