Properly charging your boat battery is essential for maintaining reliable power on your boat. Boat batteries are different from car batteries as they are responsible for additional power needs. They power the lights, gauges, pumps, and other electronics on board. Therefore, it is crucial to know how to charge them correctly to ensure your boat runs smoothly. This article will provide a comprehensive guide on how to properly charge boat batteries, including the different types of chargers, the charging process, and essential maintenance tips.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Battery type | Deep-cycle marine battery |
| Battery chemistry | Lead-acid, lithium, AGM |
| Voltage | 12V |
| Charging temperature | Optimal: above freezing |
| Safe charging temperature range | -4°F to 131°F (0°C to 55°C) |
| Battery terminals | Clean and free of corrosion |
| Charging time | 4 to 6 hours |
| Charging cables | Red (positive) cable connected to the red terminal, black (negative) cable connected to the black terminal |
| Charging process | Plug in the charger, turn it on, and wait until the battery is fully charged |
| Disconnect process | Unplug the charger, remove the black cable, then the red cable |
What You'll Learn

Choosing the right charger
Onboard vs. Portable Chargers
The first decision to make is whether to go for an onboard or a portable charger. Onboard chargers are permanently installed and connected to the boat's electrical system, offering automatic charging. They are ideal if you use your boat near shore power sources or marinas as they eliminate the need to carry a portable charger. On the other hand, portable chargers are versatile and can be used anytime, anywhere. They are also more cost-effective.
Compatibility
Whether you choose an onboard or portable charger, compatibility with your battery is crucial. First, identify the voltage of your battery, typically indicated on the battery itself. Your charger should match this voltage. For example, most marine batteries are 12 volts, so you would need a 12V charger.
Next, consider the battery's capacity, measured in ampere-hours (Ah). The charger's amperage output should be around 10-20% of the battery's capacity. For instance, a 100Ah battery would require a charger with an output of 10-20 amps.
If you have multiple batteries, the charging setup becomes more complicated. The way the batteries are connected in your electrical system will determine the charger requirements. Batteries connected in series will have their voltages added together, so you need a charger compatible with the higher voltage. For example, two 12-volt batteries in series require a 24-volt charger.
On the other hand, batteries connected in parallel will have the same voltage but increased capacity. In this case, the charger should be able to handle the combined amperage needs. So, two 100Ah batteries in parallel would require a charger suitable for a 200Ah battery bank.
Smart Chargers
Smart chargers are an excellent choice for marine batteries due to their advanced technology. They employ a multistage charging approach, including bulk, absorption, and float stages, optimising the charging process and safeguarding the battery's longevity. They prevent overcharging by gradually reducing the charging current as the battery nears full capacity.
Battery Type
The type of battery you have will also determine the right charger. Deep cycle batteries, for instance, require a specific charging regimen with a multi-stage charging process. Overcharging or undercharging can significantly impact their lifespan.
Lithium marine batteries, on the other hand, have a different charging profile. They require a carefully controlled charging process, with built-in battery management systems that prevent overcharging and overheating. They can handle higher charge and discharge rates and offer faster charging times than traditional deep cycle batteries.
Other Considerations
When choosing a charger, also consider the following:
- Charging speed: Some chargers are designed to charge batteries faster than others.
- Number of batteries: If you have multiple batteries, you may need a bank charger to charge them simultaneously.
- Charging conditions: High and low temperatures can affect your marine battery. Lithium batteries are the most resilient, but it's best to charge them above freezing.
- Special features: Some chargers have additional features like Bluetooth connectivity, LED charge status indicators, or dedicated apps to monitor charging progress.
In summary, choosing the right boat battery charger involves considering factors such as compatibility, battery type, charging speed, and special features. By selecting a charger that meets your specific needs, you can ensure efficient and safe charging, prolonging the lifespan of your boat battery.
Handicap Boating: Free Launching for Differently-Abled Sailors
You may want to see also

Selecting the right time
- Temperature: Charging a boat battery within the appropriate temperature range is vital. Lithium-ion batteries, for instance, perform best when charged in temperatures above freezing. While they can be charged at temperatures as low as below freezing (-4°F to -131°F (-20°C to -55°C) without sustaining damage, it's still recommended to maintain a temperature above freezing whenever possible. This ensures efficient charging and helps extend the battery's lifespan.
- Convenience: Consider your boating habits and schedule when selecting a charging time. If you frequently use your boat, aim to charge the battery during periods when it's not in use. This could be overnight, during the early morning, or while you're preparing for your next boating excursion. By choosing a time that aligns with your schedule, you can ensure the battery is fully charged and ready for your next outing.
- Charging Duration: Keep in mind that charging a boat battery can take several hours, typically ranging from four to six hours to reach a full charge. Therefore, selecting a charging time when you can leave the battery undisturbed for this duration is essential. This will prevent interruptions to the charging process, ensuring a complete and efficient charge.
- Charging Conditions: Choose a charging time that allows you to monitor the battery's progress and maintain the appropriate conditions. This includes keeping the battery in a well-ventilated area to prevent the buildup of explosive hydrogen gas and avoiding extreme temperatures that can affect the battery's performance and lifespan. By selecting a time when you can oversee the charging process, you can also promptly address any issues that may arise.
- Regular Charging Schedule: Establishing a regular charging routine is beneficial for battery maintenance. Aim to select charging times that align with your regular schedule or daily routines. For example, you could make it a habit to charge the battery every evening after returning from your boating trip or at a specific time each week. This helps ensure that your battery stays adequately charged and well-maintained.
By considering these factors when selecting the right time to charge your boat battery, you can optimize the charging process, maintain battery health, and ensure reliable power for your boat's electrical systems.
The Boat Race: UK's Historic Rowing Event Date
You may want to see also

Cleaning the battery terminals
To clean your battery terminals, start by turning off your boat's main power switch to avoid any electrical accidents while you work. Next, use a clean cloth or towel to wipe down the battery terminals, removing any corrosion, dirt, or grease. You can also use a wire brush to gently scrub away any built-up residue. If the terminals are particularly dirty or corroded, you may need to use a specialised battery terminal cleaning solution, which you can apply with a brush or cloth.
Once the terminals are clean, you can improve the connection by applying a small amount of terminal grease or protective spray. This will help to prevent future corrosion and ensure optimal charging.
It is important to regularly clean and maintain your battery terminals, as corrosion can inhibit proper charging and reduce the lifespan of your battery. By keeping the terminals clean, you can ensure efficient charging and maximise the performance of your boat batteries.
The Ultimate Guide to Finishing a Painted Boat
You may want to see also

Connecting the charger
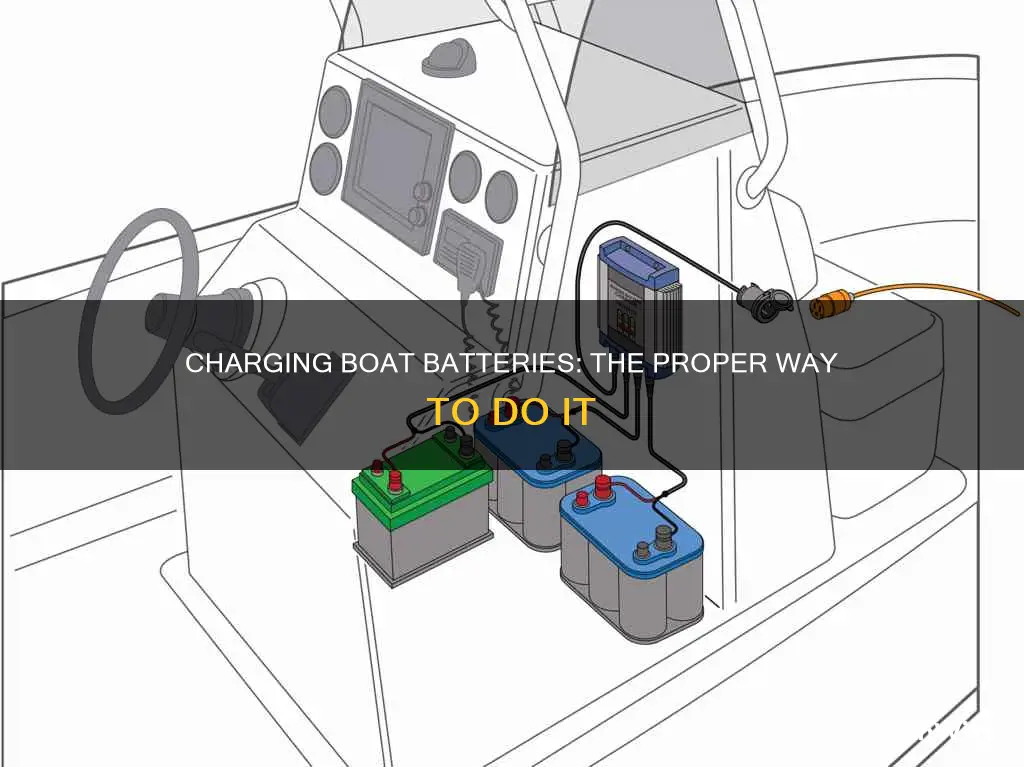
Identify the Battery Terminals: Before connecting the charger, you need to identify the positive and negative terminals on your boat battery. These terminals are usually marked with colours and symbols for easy identification. The positive terminal is typically marked with a red colour or a "+" sign, while the negative terminal is marked with a black colour or a "-" sign.
Connect the Charger Cables: Once you have identified the terminals, you can proceed to connect the charger cables. Take the red cable, which is the positive cable, and connect it to the positive terminal of the battery. Ensure a secure connection by clamping it tightly to the terminal. Next, take the black cable, which is the negative cable, and connect it to the negative terminal of the battery in the same manner.
Plug In the Charger: After both cables are securely connected to the corresponding terminals, it's time to plug in the charger. Insert the charger's plug into a power outlet or a power source, such as a 120-volt outlet for onboard chargers. Make sure the power source can provide sufficient power for the charging process.
Turn On the Charger: Once the charger is plugged in, turn it on to start the charging process. Some chargers may have a power button or switch, while others may start automatically. Refer to the instructions provided with your charger to understand its specific functionality.
Monitor the Charging Process: Depending on the type of charger you are using, you may need to monitor the charging process. For smart chargers, you can usually "set it and forget it," as they are designed to stop charging automatically once the battery is fully charged. However, for lead-acid chargers, you may need to set a timer and manually disconnect the charger once the battery is fully charged.
Safety Considerations: Always exercise caution when connecting and using a boat battery charger. Ensure that the connections are secure and correct to avoid any electrical issues. Additionally, be mindful of the charging environment and follow safety guidelines provided by the manufacturer. Keep the area well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of explosive gases.
By following these detailed steps for connecting the charger, you can ensure that your boat battery is charged effectively and safely. Remember to refer to your specific charger's instructions and safety guidelines for the best results.
The Owner of Miller Time Boat: Lake Ozark's Sensation
You may want to see also

Disconnecting the charger
Step 1: Unplug the Charger
Once your battery is fully charged, the first step is to unplug the charger from the power source. This is a simple process, but it is important to do it carefully to avoid any accidental disconnections that could interrupt the charging process.
Step 2: Remove the Negative Cable
After unplugging the charger, it's time to remove the negative cable from the battery terminal. This step is essential for safety reasons. Always make sure to disconnect the negative cable first, as it can help prevent sparks and reduce the risk of short circuits.
Step 3: Remove the Positive Cable
Now, you can proceed to remove the positive cable. Disconnect the red cable from the positive terminal of the battery. It is important to follow the correct sequence of removing the cables to avoid any potential issues.
Step 4: Verify the Order of Disconnection
Before putting away the charger, double-check that you have disconnected the cables in the correct order. The correct sequence is to first disconnect the black (negative) cable, followed by the red (positive) cable. This is an important safety measure to prevent any damage to the battery or the charger.
Step 5: Clean the Battery Terminals
After disconnecting the charger, take a moment to clean the battery terminals. Use a clean cloth or towel to wipe away any dirt or corrosion that may have built up during the charging process. This step helps maintain a good connection and ensures efficient charging in the future.
Step 6: Store the Charger Safely
Finally, store your charger in a safe and dry place. Keep it away from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight. Storing the charger properly will help ensure its longevity and maintain its functionality for future use.
Storing Your Boat: Tips for Safe and Secure Storage
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
You should use a deep-cycle marine battery charger, specifically designed for lead-acid batteries. Car chargers are not suitable as their higher voltage can damage boat batteries.
There are two types of boat battery chargers: onboard and portable. Onboard chargers are permanently installed on the boat and connected directly to the electrical system, whereas portable chargers are compact and versatile, designed to be carried on board or used on land.
First, identify the positive and negative terminals on your battery, usually marked with a plus (+) and minus (-) sign. Then, connect the charger’s positive clamp to the positive terminal and the negative clamp to the negative terminal.
A marine battery typically takes about four to six hours to charge from 0% to 80%.
Regularly check and clean your battery’s terminals to prevent corrosion, which can inhibit proper charging. Always keep the battery fully charged and store it in a cool, dry place.







