Charging a boat battery is a crucial aspect of ensuring a seamless boating experience. Boat batteries are responsible for powering lights, gauges, pumps, and other electronics on board. It is important to select the right type of charger, such as onboard or portable, and ensure compatibility with the boat battery. The charging process involves connecting the charger to the battery terminals, plugging it in, and allowing it to charge fully before disconnecting. Maintaining a full charge, regular maintenance, and proper storage are essential for extending the lifespan of boat batteries.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Battery Type | Deep-cycle |
| Charging Steps | 1. Choose the right charger; 2. Select the right time; 3. Clean the battery terminals; 4. Connect the battery charger; 5. Disconnect the charger |
| Charger Types | Onboard, Portable |
| Onboard Chargers | Permanently installed, automatically charge, monitor battery condition and adjust charging rate |
| Portable Chargers | Compact, versatile, manual, automatic, smart chargers |
| Charger Voltage/Amps | 12V charger is compatible with a 12V 100ah battery |
| Charging Temperature | Optimal temperature for Ionic Lithium Batteries is above freezing |
| Charging Time | 4-6 hours |
What You'll Learn

Choosing the right charger
Compatibility
First and foremost, ensure that your charger is compatible with your boat battery. Check the voltage of your battery, typically indicated on the battery itself. Your charger should match this voltage. For example, most marine batteries operate at 12 volts, so a charger designed for this voltage would be suitable.
Battery Capacity and Amperage
Consider the battery's capacity, measured in ampere-hours (Ah). The charger's amperage output should be appropriate for your battery's capacity. A good rule of thumb is to select a charger with an amperage output that is around 10-20% of the battery's capacity. For instance, if your battery has a capacity of 100Ah, a charger with an output of 10-20 amps would be a good match.
Type of Charger: Onboard or Portable
Boat battery chargers can be broadly categorized into two types: onboard and portable. Onboard chargers are permanently installed on the boat and connected directly to the electrical system, offering automatic charging. They are convenient if you frequently use your boat near shore power sources or marinas. On the other hand, portable chargers are versatile and can be carried on board or used on land when docked. They are usually more affordable and are ideal if you require flexibility or have limited storage space on your boat.
Smart Chargers
Smart chargers are an excellent option for marine use due to their advanced technology. These chargers employ a multistage charging approach, optimising the charging process and prolonging battery life. They prevent overcharging by gradually reducing the charging current as the battery nears full capacity. Smart chargers are available in both onboard and portable varieties, and they can be used with various battery types, including lithium and lead-acid batteries.
Battery Chemistry
Different types of boat batteries have distinct chemical compositions and characteristics, which require specific charging regimens. For example, deep cycle marine batteries, typically lead-acid-based, require a multi-stage charging process, including bulk, absorption, and float stages, to ensure optimal performance and longevity. On the other hand, lithium marine batteries have built-in battery management systems that prevent overcharging and overheating, allowing for faster charging times.
Charging Speed
If you're looking for a quick charging solution, consider the LithiumHub Ionic chargers, which are designed specifically for lithium batteries and can charge them much faster. These chargers are ideal for competitive fishermen and boaters who want to spend less time charging and more time on the water.
Number of Batteries
If you have multiple batteries on your boat, you'll need a charger that can accommodate them all. Some chargers can charge multiple batteries simultaneously, like the LithiumHub 4 Bank Charger, which can charge up to four 12V lithium batteries at once.
Charging Conditions
Consider the temperature conditions under which you'll be charging your boat battery. High and low temperatures can impact the charging process. Lithium batteries are the most versatile and can be safely charged at temperatures ranging from -4°F to 131°F (0°C to 55°C). However, for optimal performance, it is recommended to charge above freezing temperatures.
Cost and Budget
Finally, consider the cost of the charger. Boat battery chargers can range from $100 to $500 or more, depending on their size, power requirements, and additional features. Choose a charger that fits within your budget and offers the best value for your specific needs.
Winterizing Your Boat: Gas Tank Maintenance
You may want to see also

Selecting the right time
Temperature Conditions
The temperature of your battery's surroundings plays a significant role in determining the right time for charging. Lithium-ion batteries, for example, perform best when charged in temperatures above freezing. While it is possible to charge them at temperatures as low as below freezing (-4°F to -131°F (-20°C to -55°C) without causing damage, keeping them above freezing is ideal. This ensures efficient charging and helps extend the lifespan of your battery.
Battery Level
Monitoring the level of charge in your boat battery is essential for selecting the right time to recharge. Ideally, you should keep your battery charged to a healthy level and recharge it as soon as possible after it falls below 50% capacity. This practice helps prevent deep discharge, which can reduce the lifespan of your battery. Repeated shallow discharge (5-10%) can also impact the battery's longevity, so it's important to recharge promptly to maintain optimal performance.
Charging Duration
Consider the duration of time required to charge your boat battery. Depending on the type of charger and battery, charging can take several hours. For example, a marine battery typically charges from 0% to 80% in about four to six hours. Therefore, selecting a time when you can leave the battery charging uninterrupted until it reaches full capacity is essential. This ensures that you don't interrupt the charging cycle and helps maintain the health of your battery.
Convenience and Accessibility
Choosing a convenient time to charge your boat battery is also important. If you opt for a portable charger, you may want to select a time when you're near a power source, whether at home or at a marina. This ensures that you have easy access to the necessary resources for charging. Additionally, if you have a busy schedule, selecting a charging time that aligns with your availability makes the process more manageable.
Charging Frequency
Determining the right time to charge your boat battery also involves considering the frequency of charging. Boat batteries, especially those used frequently, require regular charging to maintain their performance. If you use your boat daily or several times a week, establishing a charging routine becomes crucial. Selecting specific days or times when you can consistently charge your battery helps ensure it stays in top condition and is ready for your next outing.
In conclusion, selecting the right time to charge your boat battery involves considering temperature conditions, battery level, charging duration, convenience, and charging frequency. By taking these factors into account, you can optimize the charging process and maintain the health and longevity of your boat battery.
Exploring the Cayman Islands and Jamaica by Boat
You may want to see also

Cleaning the battery terminals
To clean your battery terminals, start by disconnecting the battery. This will ensure your safety and prevent any accidental short circuits. Once the battery is disconnected, use a wire brush or a stiff-bristled brush to scrub the terminals and remove any corrosion or dirt buildup. You can also use a specialised battery terminal cleaning brush for this purpose. If the terminals are heavily corroded, you may need to use a stronger cleaning solution, such as a mixture of baking soda and water, or a commercial battery terminal cleaner. Apply the cleaning solution to the terminals and use the brush to scrub away the corrosion.
After scrubbing the terminals, wipe them down with a clean, dry cloth to remove any remaining residue. You can also use a small amount of petroleum jelly or a corrosion-inhibiting spray on the terminals to help prevent future corrosion.
Once the terminals are clean, inspect them for any signs of damage, such as cracks or fraying. If the terminals are damaged, they may need to be replaced before you can continue with the charging process.
By taking the time to clean and inspect your battery terminals, you can help ensure that your boat battery charges efficiently and effectively, and you can also help extend the overall lifespan of your battery.
Bass Boat Splurge: The Ultimate Expensive Buy
You may want to see also

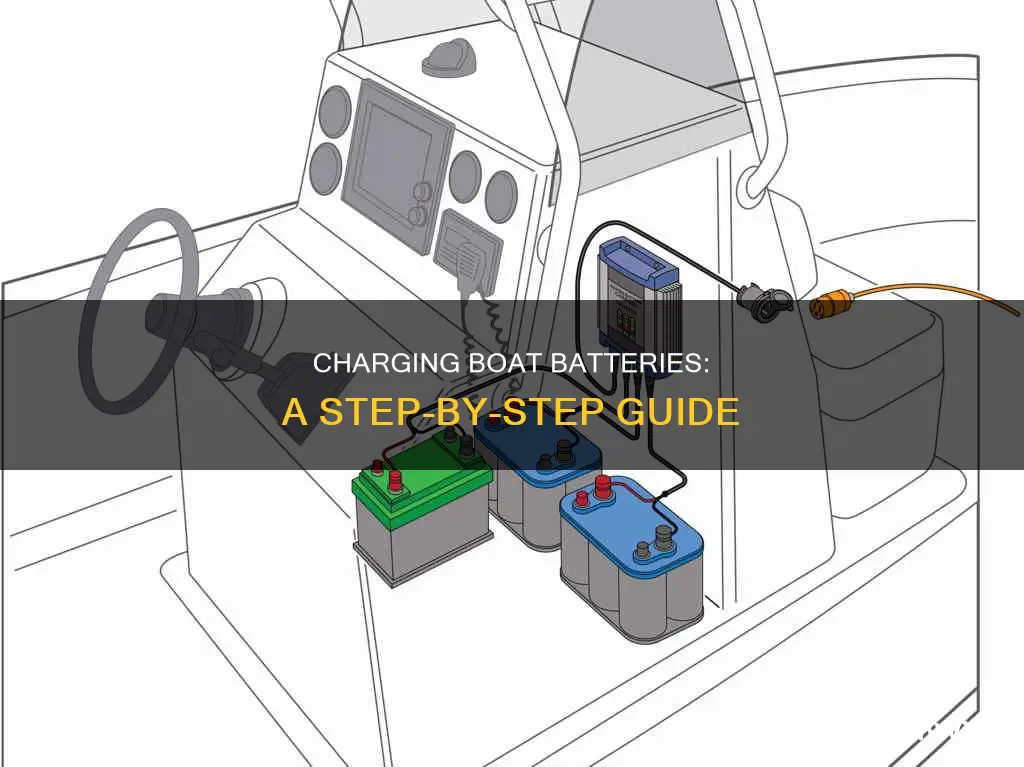
Connecting the battery charger
Ensure Proper Colour-Coding:
Before you begin, it's important to identify the colours of the cables and terminals. The charger should have a red (positive) cable and a black (negative) cable. The battery terminals will also have corresponding colours, with a red terminal for positive and a black terminal for negative. This colour-coding ensures that you make the correct connections.
Connect the Red Cable:
Take the red (positive) cable from the charger and carefully connect it to the red (positive) terminal on the battery. Make sure the connection is secure and firm. This initial connection is important as it establishes the flow of positive charge into the battery.
Connect the Black Cable:
Next, take the black (negative) cable from the charger and connect it to the black (negative) terminal on the battery. Again, ensure that the connection is secure. This completes the circuit, allowing the battery to receive the charge.
Plug In and Turn On the Charger:
Once the cables are properly connected to the battery terminals, it's time to plug the charger into a power source. Depending on the type of charger you have, this could be an electrical outlet or a different power source. After plugging it in, turn on the charger. Some chargers may have a power button, while others may activate automatically once plugged in.
Monitor the Charging Process:
At this point, the battery should be charging. If you're using a smart charger, it will automatically stop charging once the battery is fully charged. Smart chargers are designed to prevent overcharging and make the process more convenient. However, if you're using a lead-acid charger, you'll need to monitor the charging process and disconnect the charger manually once the battery is fully charged.
Disconnecting the Charger:
When the battery is fully charged, it's time to disconnect the charger. First, unplug the charger from the power source. Then, carefully remove the cables from the battery terminals, starting with the black (negative) cable, followed by the red (positive) cable. It's important to maintain the correct order when disconnecting to ensure a safe and proper disconnection.
Remember to follow safety precautions when handling batteries and chargers. Always wear protective gear, such as gloves and eye protection, and ensure proper ventilation during the charging process. By following these detailed steps, you can confidently connect your boat battery charger and keep your marine adventures fully powered!
Streaming 'The Boys in the Boat': Where to Watch?
You may want to see also

Disconnecting the charger
Unplug the Charger: Once your battery is fully charged, the first step is to unplug the charger from the power source. This is a simple process, but it is essential to cut off the power supply before proceeding with the next steps.
Disconnect the Cables: After unplugging, you can move on to disconnecting the cables from the battery terminals. It is important to follow the correct sequence when doing this. First, remove the black cable, which is the negative cable, from its corresponding black terminal. Then, proceed to detach the red cable, which is the positive one, from the red terminal. By following this order, you reduce the risk of any potential sparks or short circuits.
Cable Management: Once the cables are disconnected, it is good practice to properly manage and store the cables. Ensure that the cables are not tangled and that they are kept in a safe place, away from any moisture or potential sources of damage. Proper cable management will help extend the life of your charging equipment.
Battery Inspection: Before concluding the process, take a moment to inspect the battery terminals. Look for any signs of corrosion, dirt, or damage. If you notice any corrosion or dirt build-up, it is important to clean the terminals to maintain optimal performance. You can use a suitable cleaning agent and a brush to gently remove any residue.
Final Checks: Before considering the charging process complete, double-check that the battery is securely mounted and that all connections are tight. Ensure that the battery is stable and will not shift during boat operations. This will help prevent any vibrations or movements that could potentially loosen connections or cause damage.
By following these steps for disconnecting the charger, you can ensure that your boat battery is charged safely and effectively. Remember always to exercise caution when working with electrical equipment and batteries, and refer to manufacturer guidelines for specific instructions related to your battery and charger.
Preventing Engine Freeze: Tips for Boat Owners
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
First, ensure the battery terminals are clean. Then, connect the red (positive) cable to the red terminal, and the black (negative) cable to the black terminal. Plug in the charger and turn it on. Once the battery is fully charged, unplug the charger, and remove the cables in reverse order (black, then red).
A marine battery will usually take around four to six hours to charge from 0% to 80%.
A marine battery will usually hold its charge for about six months, depending on the make/model and type of battery.
Yes, you can use a portable charger to charge your boat's battery while it's afloat.







