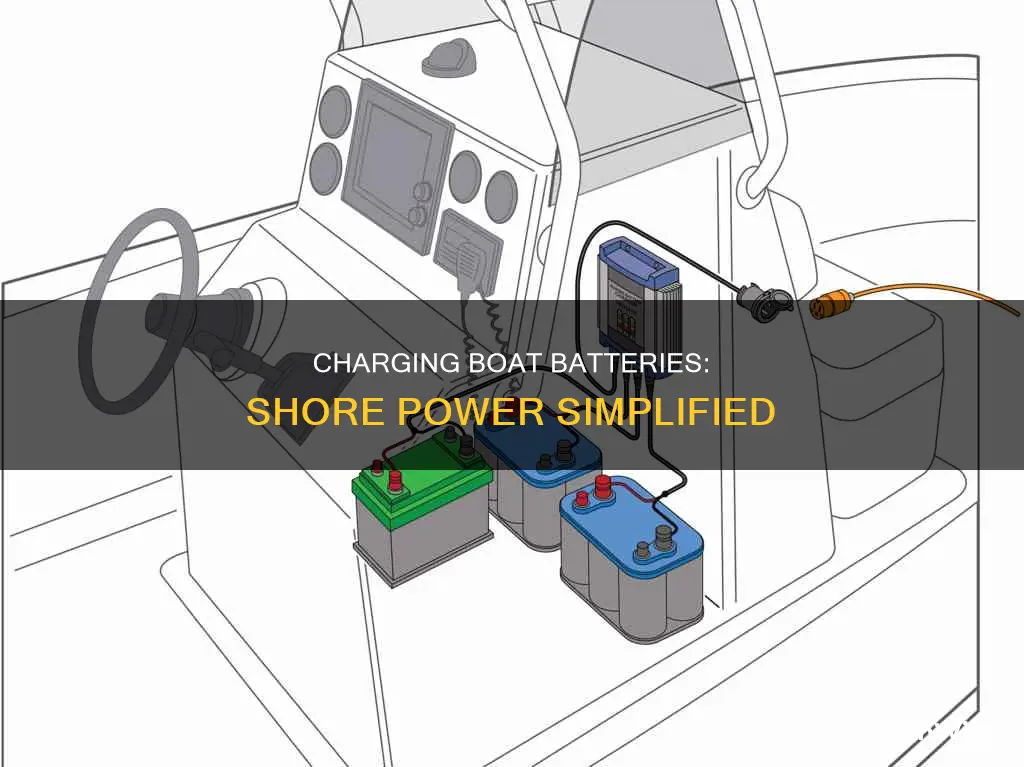
Charging a boat battery using shore power is a simple process that can save boat owners from a lot of trouble. Shore power refers to the electrical plug-ins located at boat slips, providing a reliable source of electricity for boaters. This power source is especially useful for charging boat batteries, which is crucial for a seamless boating experience.
To charge a boat battery using shore power, follow these steps:
1. Connect Your Boat to Shore Power: Properly secure your boat in its slip or tie it to the dock. Use a shore power cord to plug your boat into the dock's electrical outlet, ensuring all electrical switches and circuits are turned off.
2. Check Battery Voltage: Before charging, check your battery voltage with a multimeter to ensure it's not fully charged or discharged. If it reads less than 12 volts, it needs charging.
3. Turn on Your Battery Charger: Locate the on/off switch on your boat charger and turn it on. Set the charger to the appropriate voltage for your battery, as specified in the owner's manual.
4. Monitor the Charging: Keep an eye on the charging process and periodically check the voltage. Intervene if the voltage gets too high to avoid overcharging, which can damage the battery.
5. Disconnect and Return to Battery Power: After a few hours, your battery should be fully charged. Turn off the charger, disconnect it from shore power, and switch back to battery power. Test your boat's electrical systems and the battery voltage to ensure everything is functioning correctly.
By following these steps, boat owners can ensure their batteries are charged and well-maintained, providing a reliable power source for their boating adventures.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| What is shore power? | Electrical plug-ins located at boat slips to provide boaters with a reliable source of electricity |
| Type of power | AC (alternating current) power |
| Use of shore power | Charging boat batteries, powering appliances such as TVs, microwaves, and hair dryers |
| Onboard charging methods | Shore power charging, offshore charging, alternator charging |
| Portable charging methods | AC to DC Charger, solar panels, engine charging via an alternator |
| Battery types | Lead-acid, lithium |
| Charging process | Connect to shore power, check battery voltage, turn on battery charger, monitor charging, disconnect and return to battery power |
| Battery maintenance | Avoid overcharging, maintain a full charge, regular maintenance, proper storage, follow manufacturer's instructions |
What You'll Learn

Connect boat to shore power
Shore power refers to the electrical plug-ins located at boat slips, providing boats with a reliable source of electricity. It is important to ensure that the amperage of your electrical system matches the amps from the shore power outlet, and if not, use the right adapters.
- Check the shore power cable and socket for any damage. Ensure that the cable is designed for use with boats and has the 'CE' marking. Do not use the cable if it is damaged or repaired with electrical tape. Inspect if any cable strands are exposed or if the inner wire coloured insulation is visible.
- Connect the boat end of the shore power cable first. The shore power cable should be fully uncoiled to avoid overheating.
- Plug the shore power cable into the receptacle on your boat.
- Turn on the breaker on the pedestal on the dock. An indicator light will notify you that you are receiving power.
- Go to your breaker panel and flip the "Shore 1" switch to the "on" position. This will power up your boat, and a green indicator light will confirm this.
- If you need to use a second shore power cord, disengage the "parallel" switch. The "Shore 2" button will turn green, indicating that it is on.
- You can now activate different devices and areas of your vessel, such as air conditioning and water pumps.
By following these steps, you can safely connect your boat to shore power and utilise the electrical amenities available at the dock.
A Brief History of Boat Launches and Their Evolution
You may want to see also

Check battery voltage
Checking your battery voltage is an important step before charging your boat battery using shore power. This step ensures that your battery is not fully charged or fully discharged. To check the voltage, you can use a multimeter. If the reading is less than 12 volts, it indicates that your battery needs to be charged.
It is important to note that different types of batteries have different voltage requirements. For example, most marine batteries have a voltage of 12 volts. However, it is always recommended to refer to your battery's specifications to determine the correct voltage. Additionally, when adding multiple batteries to your marine system, the charging process becomes more complex. The voltage and amperage requirements of your charger will depend on how the batteries are connected (in series or parallel).
When batteries are connected in series, their voltages add up. For instance, two 12-volt batteries in series result in a total voltage of 24 volts. In this case, a higher-voltage charger is needed. On the other hand, when batteries are connected in parallel, the voltage remains the same, but the capacity (amp-hours) doubles. Therefore, the charger should be capable of handling the combined amperage requirements of the parallel-connected batteries.
By regularly checking your battery voltage and ensuring it is within the appropriate range, you can maintain the health of your battery and ensure it is ready for your next boating adventure.
The Ultimate Guide to Boat Tube Rope Lengths
You may want to see also

Turn on battery charger
Turning on your battery charger is a simple process, but it's important to follow the correct steps to ensure your boat battery charges efficiently and safely. Here's a detailed guide on how to turn on your battery charger when using shore power:
Step 1: Understand Your Setup
Before turning on your battery charger, it's crucial to understand your boat's electrical system and battery setup. This includes knowing the type of batteries you have (lead-acid or lithium) and how they are connected (in series or parallel). Additionally, check if your boat has a house power system or shore power connections. Most boats will have a battery charger included in the house power system, but smaller boats might require an additional charger.
Step 2: Connect to Shore Power
Securely dock your boat and turn off all electrical switches and circuits. Use a shore power cord to connect your boat to the dock's electrical outlet. This provides AC (alternating current) power to your boat, which you will use to charge your batteries.
Step 3: Check Battery Voltage
Use a multimeter to check your battery voltage. This step is important to ensure your battery needs charging. If the voltage reads less than 12 volts, you should proceed to charge your battery.
Step 4: Turn on the Battery Charger
Now it's time to turn on your battery charger. Locate the charger unit and ensure it is turned on using the on/off switch. Set the charger to the appropriate voltage for your battery. Refer to your owner's manual to determine the correct voltage setting.
Step 5: Monitor the Charging Process
Once the charger is on, periodically monitor the voltage during the charging process. Overcharging can damage your battery, so keep an eye on the voltage to ensure it doesn't climb too high. Similarly, if the charger isn't delivering enough voltage or amperage, it may not fully charge the battery.
Step 6: Disconnect and Return to Battery Power
After a few hours, your battery should be fully charged. Turn off the charger, disconnect it from shore power, and return to using battery power. Test all electrical systems to ensure they are functioning correctly, and verify the battery voltage is at the appropriate level.
Remember to follow these steps carefully and never leave your battery unattended while charging. Keeping your boat battery charged will ensure a smooth and enjoyable boating experience.
Boat Stolen? Here's What You Need to Do
You may want to see also

Monitor charging process
Monitoring the charging process is crucial to ensure your boat battery charges efficiently and safely. Here are some detailed instructions to guide you through the monitoring process:
- After connecting your boat to shore power and turning on the battery charger, pay close attention to the charging process. It is important to periodically check the voltage level to ensure it remains within a safe range.
- Be cautious of overcharging. If the voltage climbs too high, it can damage your battery. Modern smart chargers are designed to prevent overcharging by automatically adjusting the charging process. However, it is still essential to keep an eye on the voltage to ensure it doesn't exceed the safe limit.
- On the other hand, if the charger isn't delivering enough voltage or amperage, your battery may not reach a full charge. In this case, you may need to adjust the settings on the charger or consult a professional for advice.
- Depending on the type of battery you have, the charging time will vary. Lead-acid batteries can take up to 10 hours to charge fully, while lithium-ion batteries usually charge much faster. Keep this in mind and be prepared to wait if necessary.
- If you have multiple batteries or a complex electrical system, the charging process may be more involved. Consult your boat's manual or seek advice from a marine electrician to ensure you're monitoring the process correctly.
- Finally, remember to disconnect the charger and return to battery power once the battery is fully charged. Test the battery's voltage to ensure it's at the appropriate level, and make sure all electrical systems are functioning correctly.
Spotting Fake Sperry Boat Shoes: A Guide to Authentic Details
You may want to see also

Disconnect charger and return to battery power
Once your battery is fully charged, it's time to disconnect the charger and return to battery power. This process is simple but important to ensure your boat's electrical systems are functioning correctly. Here are some detailed instructions to guide you through the process:
Firstly, turn off your battery charger. Locate the on/off switch on the unit and ensure it is turned off. This is crucial to prevent overcharging, which can damage your battery. Next, disconnect the charger from shore power. Carefully unplug the shore power cord from the dock's electrical outlet and your boat. It is important to handle the cords properly to avoid any damage.
Now, return to battery power. Turn on your boat's electrical systems and ensure everything is functioning correctly. Test each component, such as the lights, GPS, radios, and any other electronic devices. Check that they are receiving adequate power and operating as expected.
It is important to test the battery's voltage to ensure it is at the appropriate level. Use a multimeter to check the voltage. It should read 12 volts or higher, indicating a full charge. If the voltage is lower than expected, you may need to allow for more charging time or adjust your charging settings.
Additionally, regular maintenance of your battery is essential. Periodically check the battery's state of charge, electrolyte levels (for flooded batteries), and the condition of the terminal connections. Clean the terminals if they are corroded and ensure all connections are tight and secure.
Finally, proper storage of your battery is crucial, especially if your boat will be unused for an extended period. Consider using a battery maintainer or trickle charger to keep the battery in good condition and store it in a cool, dry place. Always follow the manufacturer's instructions and guidelines for charging and maintaining your specific battery type.
Repairing a Leaky Boat Hull: Quick and Easy Fixes
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Shore power refers to the electrical plug-ins at boat slips that provide a reliable electricity source for boaters.
Use a shore power cord to plug your boat into the dock's electrical outlet. Ensure all electrical switches and circuits are off before connecting.
Shore power is AC (alternating current) power, which is the type of electricity supplied through the electrical grid.
Yes, but be cautious. A "dead" battery may be damaged. It's recommended to use a marine battery charger, and always charge your batteries after each use of the boat.
It depends on the type of battery. Lead-acid batteries can take up to 10 hours and need to be fully charged to avoid damage. Lithium-ion batteries take significantly less time and are not as susceptible to damage if not fully charged.







