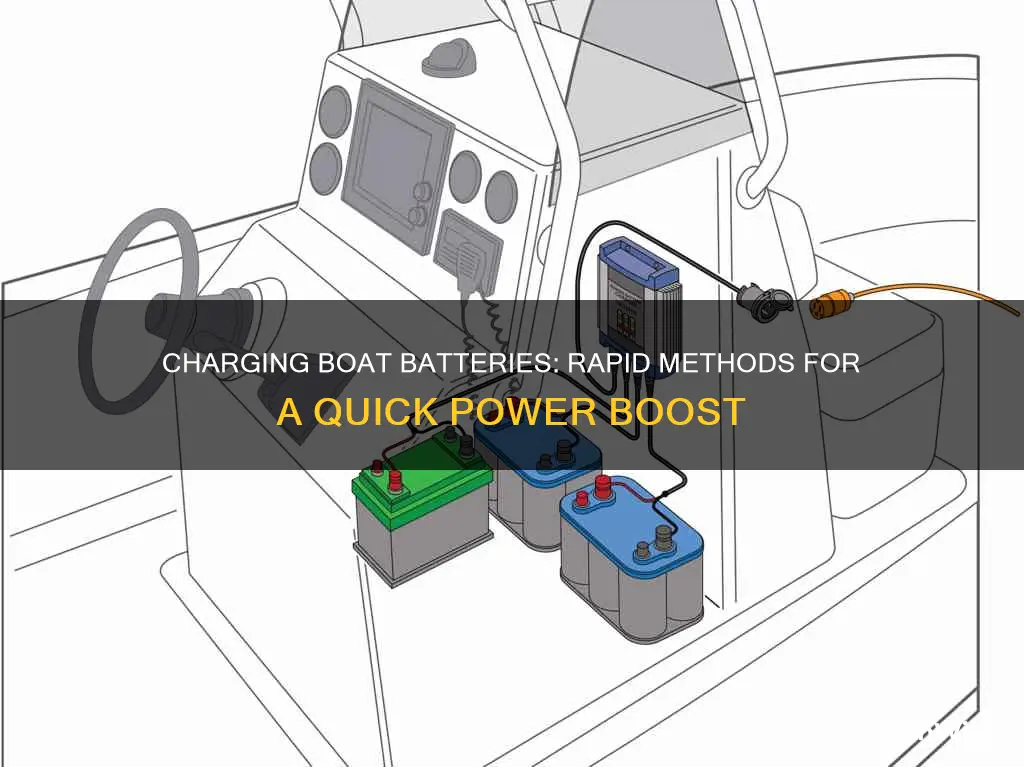
Charging a boat battery is an essential skill for boat owners, as boat batteries are responsible for powering lights, gauges, pumps, and other electronics on board. There are two main types of boat battery chargers: onboard and portable. Onboard chargers are permanently installed on the boat and connected directly to the boat's electrical system, offering automatic charging. Portable chargers, on the other hand, are known for their convenience and can be used anytime, anywhere. When choosing a charger, it is important to match the charger's voltage to the boat battery's voltage. Additionally, it is recommended to keep the battery terminals clean and to avoid overcharging the battery.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Types of boat battery chargers | Onboard, Portable |
| Optimal charging temperature | Above freezing for ionic lithium batteries |
| Charging time | 4-6 hours to charge from 0% to 80% |
| Battery voltage | 12V |
| Battery capacity | 70-80 Amp-hours |
| Maximum recommended charging rate | 1/3rd of the capacity, about 23 Amps |
| Float-charge voltage | 13.6-13.7V |
| Battery maintenance | Keep fully charged, avoid partial charge, avoid overcharging |
What You'll Learn

Onboard vs portable chargers
Onboard and portable chargers are the two main types of boat battery chargers. The choice between the two depends on factors such as boating habits, frequency of use, and budget. Here is a detailed comparison between the two:
Onboard Marine Battery Chargers
Onboard marine chargers are permanently installed on the boat and connected directly to the boat's electrical system. They offer automatic charging by continuously monitoring the battery's condition and adjusting the charging rate. Onboard chargers are ideal for boaters who frequently use their boats near shore power sources or marinas as they eliminate the need to carry and connect a portable charger each time.
Onboard chargers can have up to four separate battery chargers (called "banks") housed in a single casing, allowing the charging of multiple batteries simultaneously. They are typically waterproof, corrosion-resistant, and can be mounted in damp locations. The installation process is straightforward and can be done in a few hours, although some users may prefer professional installation.
Methods of onboard charging include shore power charging (using an external power source at a marina), offshore charging (using onboard generators or alternative power sources like solar power), and alternator charging (using the boat's engine alternator).
Portable Marine Battery Chargers
Portable marine chargers are known for their convenience and portability. They can be used anytime, anywhere, and are less expensive than onboard chargers. They are compact, versatile, and suitable for various battery types. Portable chargers are essential for boaters who frequently operate far from shore power or marinas, as they enable recharging wherever the boat is anchored.
Portable chargers come in different models, including manual, automatic, and smart chargers. Smart chargers, in particular, are designed to optimise the charging process, ensuring efficient and safe charging. They use a multistage charging approach that includes bulk, absorption, and float stages, helping to speed up charging and safeguard the battery's longevity.
The decision to choose between onboard and portable chargers depends on individual needs and boating habits. Onboard chargers offer convenience and automatic charging, while portable chargers provide versatility and mobility. Budget is also a consideration, with portable chargers being more cost-effective than installing onboard systems. Ultimately, some boaters may opt for both types to have a backup power source and adapt to different scenarios.
Boat Insurance Savings: Tips for Cost-Effective Coverage
You may want to see also

Charging at the right time
Charging a boat battery requires certain conditions. The optimal charging temperature for ionic lithium batteries is above freezing, and you can charge them at temperatures of -4°F to -131°F without causing damage. If your battery is a 12V battery, most car battery chargers with an "AGM" setting will work.
To determine a battery's charging speed, you need to know the amp-hour rating of your battery and the amperage of the battery charger. You can calculate the charging time by dividing the battery's amp-hour rating by the amperage of your charger. For example, a 75Ah battery using a 7.5-amp charger will take about 10 hours to fully charge.
It is important to avoid overcharging your battery. Overcharging can cause irreparable damage and drastically shorten its lifespan. Basic battery chargers need to be monitored to ensure the battery doesn't get overcharged. However, most onboard chargers have protection against overcharging and will switch to float or maintenance mode once the battery is fully charged.
To keep your battery healthy, always keep it fully charged. Lead-acid batteries are prone to sulfation, which occurs when the battery remains partially charged for extended periods. Lithium batteries are less susceptible to this issue and can handle being partially charged better.
If you're not using your boat regularly, consider using a trickle charger to keep your battery charged. Trickle chargers allow a small amount of electricity to flow into the battery, slowly charging it over several days. They are perfect for situations with on-and-off usage, such as during the summer months. Trickle chargers can be permanently attached to your boat or used as portable chargers.
When charging your boat battery, ensure the connectors are attached properly. Look for clamp connectors with black and red tips, matching the black clamp to the negative side and the red clamp to the positive side of your battery. Most modern chargers have an indicator to let you know when the connectors are properly attached.
Triton Sea Hunt 2003: A Reliable Offshore Boat?
You may want to see also

Cleaning battery terminals
To clean your battery terminals, you'll need to disconnect the battery from the charger. The process of cleaning the terminals will depend on the type of corrosion or grime that has built up.
For a simple clean, you can use a wire brush to scrub the terminals and remove any residue or corrosion. Ensure you also clean the inside of the cable clamps, as grime can build up there too.
If the corrosion is more severe, you may need to use a specialised battery terminal cleaner, which can be purchased from most auto parts stores. These cleaners typically come in a spray bottle and are designed to dissolve corrosion and build-up on battery terminals. Simply spray the solution onto the terminals and follow the manufacturer's instructions for how long to leave it on before wiping it off.
Another method is to create a paste from baking soda and water. Apply this paste to the terminals and use a toothbrush or small wire brush to scrub away the corrosion. Rinse the terminals with clean water and dry them thoroughly before reconnecting the battery.
Once the terminals are clean, you can apply a small amount of grease or petroleum jelly to help prevent future corrosion. This will also help ensure a better connection between the terminals and the charger clamps.
It is important to regularly clean and maintain your battery terminals to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your battery. Corroded or grimy terminals can disrupt the charging process, leading to longer charge times and reduced battery efficiency.
Repairing Vinyl Boat Seats: Fixing Cracks Like a Pro
You may want to see also

Connecting the battery charger
Step 1: Identify the Terminals
Before you begin, it's important to familiarise yourself with the battery terminals. The positive terminal is usually indicated by a red colour, while the negative terminal is typically black. This colour-coding will guide you in making the correct connections.
Step 2: Connect the Charger Cables
Start by connecting the red (positive) cable from the charger to the red (positive) terminal on the battery. Ensure a secure connection by clamping or tightening the cable appropriately. Next, connect the black (negative) cable from the charger to the black (negative) terminal on the battery, following the same secure connection procedure.
Step 3: Plug In and Turn On the Charger
Once the cables are securely connected, it's time to plug the charger into a power source. Depending on the type of charger, this could be a standard 120-volt outlet or another power source, such as solar energy. After plugging in the charger, turn it on to begin the charging process.
Step 4: Monitor the Charging Process
The charging time will vary depending on the type of battery and charger you are using. Smart chargers with automatic functions will stop charging when the battery is full, and some even have Bluetooth capabilities for easy monitoring. If you are using a lead-acid charger, you will need to set a timer and manually disconnect it once the battery is fully charged.
Step 5: Disconnect the Charger
When the battery is fully charged, it's important to disconnect the charger properly. First, unplug the charger from the power source. Then, following the reverse order of connection, remove the black (negative) cable from the battery terminal, followed by the red (positive) cable. This ensures a safe disconnection process.
It is important to note that the steps outlined above are general guidelines, and specific instructions may vary depending on the type of boat battery and charger you are using. Always refer to the manufacturer's instructions and guidelines for charging and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and safety.
The Vanishing Wizard Boat: An Unraveling Mystery
You may want to see also

Disconnecting the charger
The process of disconnecting the charger begins with monitoring the charging progress. If you are using a smart charger, it may automatically stop charging once the battery is fully charged, so you don't have to worry about overcharging. However, if you are using a lead-acid charger or a basic battery charger, it's essential to keep an eye on the charging progress to prevent overcharging. Overcharging can cause irreparable damage to your battery and significantly reduce its lifespan.
Once the battery is fully charged, you can initiate the disconnection process. First, turn off the charger. This step is important as it ensures that the charging process is completely halted, and no more current flows into the battery. Then, you can proceed to disconnect the charger cables from the battery terminals. It is standard practice to disconnect the negative cable first. So, carefully remove the black cable (negative) from its corresponding black terminal. After the negative cable is safely disconnected, you can then proceed to remove the red cable (positive) from the red terminal. Always be cautious when handling the battery terminals to avoid any accidental sparks or short circuits.
It is good practice to inspect the battery terminals for any signs of corrosion or damage. If you notice any corrosion buildup, you can clean the terminals using a suitable cleaning agent and a wire brush. Maintaining clean and well-maintained battery terminals is essential for ensuring efficient charging and overall battery health.
After disconnecting the charger, it's important to properly store the charging equipment. Store the charger in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures. Ensure that the charger cables are neatly coiled and secured to avoid any tripping hazards or accidental damage. Additionally, if you are using a portable charger, keep it in a safe place to prevent theft, especially when docked or moored for extended periods.
Lastly, always refer to the manufacturer's instructions and guidelines for specific recommendations regarding the charging and maintenance of your particular battery and charger. Different batteries and chargers may have unique requirements, so adhering to the manufacturer's instructions is crucial for optimal performance and safety.
Shifter Cable Setup: Top Cable Configuration for Boats
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
To charge your boat battery quickly, use a charger designed specifically for it. You can expect a marine battery to charge from 0% to 80% in about four to six hours.
There are two types of boat battery chargers: onboard and portable. Onboard chargers are permanently installed on the boat and connected directly to the boat's electrical system, while portable chargers can be used anytime, anywhere, and are less expensive.
First, clean the battery terminals. Then, connect the red (positive) cable to the red terminal and the black (negative) cable to the black terminal. Plug in the charger and turn it on.
If you're using a smart charger, it will stop charging automatically. Otherwise, you'll need to set a timer and manually disconnect the charger.







