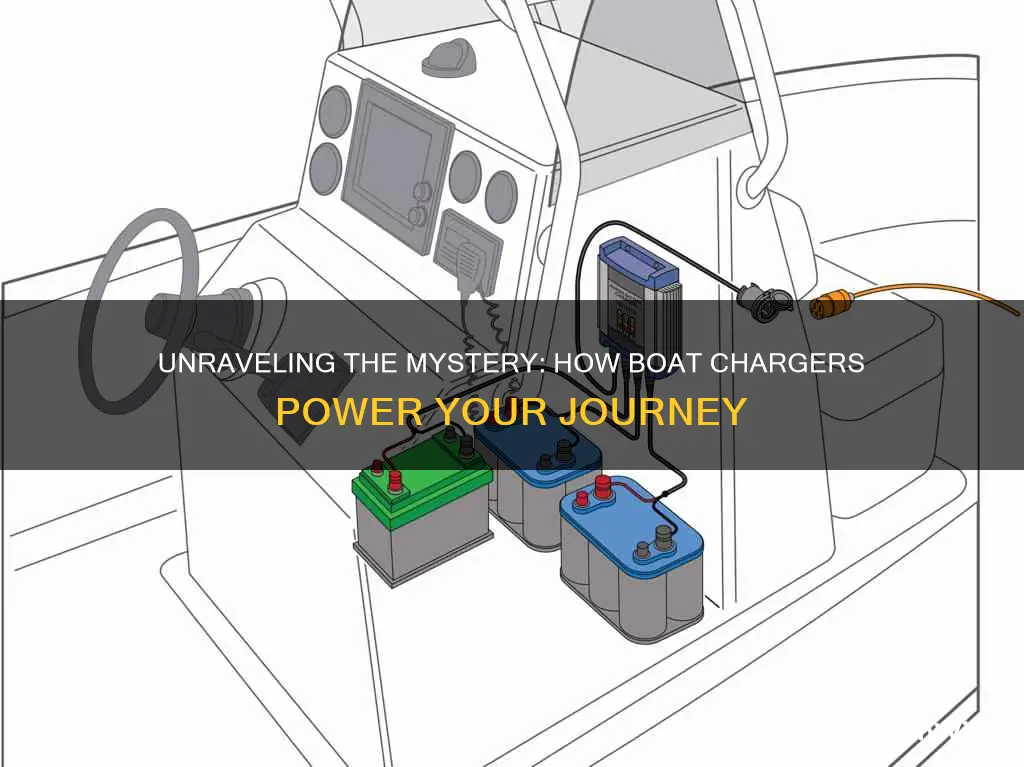
A boat charger is a device designed to replenish the battery power of boats, ensuring they remain operational during extended periods on the water. Understanding how a boat charger works is essential for boaters to maintain their vessels effectively. The charging process involves converting the electrical energy from the boat's alternator or shore power into a form suitable for the battery. This is typically achieved through a regulated voltage and current output, preventing overcharging and ensuring the battery's longevity. The charger's efficiency and safety features are crucial, as they protect the battery from damage and ensure a steady and controlled charging process. This introduction sets the stage for a more detailed explanation of the technical aspects of boat charging systems.
What You'll Learn
- Power Source: Boat chargers draw power from shore or onboard generators
- Regulation: Chargers regulate voltage to prevent overcharging and damage
- Connection: They connect to batteries via cables or direct mounting
- Charging Algorithm: Chargers use algorithms to optimize charging rates
- Safety Features: These include overcurrent protection and temperature monitoring

Power Source: Boat chargers draw power from shore or onboard generators
Boat chargers are essential devices for ensuring that your vessel's batteries remain charged and ready for use, whether you're docked at a marina or out on the open water. The power source for these chargers can vary, but the most common and practical option is to draw power from either a shore-based power supply or an onboard generator.
When a boat is docked, it can connect to a shore power supply, which is a convenient and reliable method of charging. This power source is typically provided by a marina or a dock, and it offers a steady and consistent flow of electricity. The charger on the boat then connects to this shore power, and the process of charging the batteries begins. This method is especially useful for overnight stays or when you need to keep your boat's batteries topped up for an extended period.
Onboard generators are another viable power source for boat chargers. These generators are designed to produce electricity while the boat is in motion or when shore power is not available. By utilizing an onboard generator, you can ensure that your boat's batteries are always charged, even in remote locations or during extended voyages. This setup provides a more independent and self-sufficient power solution for boaters.
The process of charging the batteries through these power sources involves a regulated flow of electricity. Boat chargers are equipped with smart technology that monitors the battery's voltage and current, adjusting the charging rate accordingly. This ensures a safe and efficient charging process, preventing overcharging and potential damage to the batteries.
In summary, boat chargers can draw power from shore-based sources or onboard generators, offering flexibility and reliability in keeping your boat's batteries charged. Understanding these power sources and their integration with chargers is crucial for boaters to maintain a fully functional and safe vessel.
The Best Way to Install Boat Tag Numbers
You may want to see also

Regulation: Chargers regulate voltage to prevent overcharging and damage
A boat charger is an essential component for any boating enthusiast, ensuring that your vessel's battery remains charged and ready for use. One of the critical functions of a boat charger is voltage regulation, which plays a vital role in preventing overcharging and potential damage to the battery. Overcharging can lead to several issues, including reduced battery lifespan, increased risk of overheating, and even safety hazards.
Voltage regulation in a boat charger is designed to maintain a consistent and optimal charging voltage for the battery. When a boat charger is connected to the battery, it monitors the voltage levels. If the voltage drops below a certain threshold, the charger will initiate the charging process, supplying the necessary power to bring the battery back up to the desired level. This automatic regulation ensures that the battery is charged efficiently without being overcharged.
The regulation process involves a sophisticated control system within the charger. It continuously measures the battery's voltage and adjusts the charging current accordingly. When the battery is fully charged, the charger will automatically reduce the charging current to a trickle or float voltage, which is typically lower than the initial charging voltage. This trickle charge helps maintain the battery's charge without overworking it.
Over time, as the battery ages, its ability to hold a charge may decrease. In such cases, the charger's voltage regulation becomes even more crucial. It compensates for the battery's reduced capacity by providing a controlled charging process. This prevents the battery from becoming overcharged, which could lead to sulfation, a condition where lead sulfate crystals form on the battery's plates, significantly impacting its performance.
In summary, voltage regulation is a critical aspect of how a boat charger works. By monitoring and adjusting the charging voltage, chargers ensure that batteries are charged safely and efficiently. This regulation feature not only extends the battery's lifespan but also contributes to the overall reliability and performance of the boating system. Understanding this process highlights the importance of using a well-regulated charger for maintaining a healthy and functional boat battery.
Boat Registration: Scottsbluff, NE — Where and How?
You may want to see also

Connection: They connect to batteries via cables or direct mounting
When it comes to charging a boat's battery, the connection method is a crucial aspect to consider. The primary way a boat charger connects to the battery is through cables or direct mounting. This connection enables the charger to supply power to the battery, ensuring it remains charged and ready for use.
The cable connection is a common and flexible approach. It involves running a cable from the charger to the battery, typically with a positive and negative terminal on the charger corresponding to the battery's terminals. This method allows for easy placement of the charger, as it can be positioned near the battery or even on a different part of the boat, as long as the cable is long enough to reach. The cable should be of an appropriate gauge to handle the current flow without overheating.
Direct mounting, on the other hand, involves physically attaching the charger to the battery. This method is often used in situations where space is limited or a more permanent solution is required. The charger is mounted directly onto the battery, usually with screws or brackets, creating a secure and stable connection. Direct mounting ensures a consistent and reliable power supply, as the charger is in constant contact with the battery. This method is particularly useful for marine applications where vibrations and movement are common.
Both connection methods have their advantages. Cable connections offer flexibility and ease of installation, allowing for different charging scenarios. Direct mounting provides a more integrated and secure solution, especially in harsh marine environments. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the boat and the user's preferences.
In summary, the connection between a boat charger and its battery is vital for efficient charging. Whether through cables or direct mounting, this connection ensures the charger can effectively supply power to the battery, keeping it charged and ready for use during boating adventures. Understanding these connection methods is essential for anyone looking to maintain and charge their boat's battery effectively.
Why Topside Paint on a Boat's Bottom is Bad
You may want to see also

Charging Algorithm: Chargers use algorithms to optimize charging rates
Boat chargers are designed to efficiently power and recharge the batteries on boats, ensuring a reliable energy source for various onboard systems. At the heart of these chargers is a sophisticated charging algorithm, a crucial component that optimizes the charging process. This algorithm is a set of instructions or a program that governs the charging behavior, ensuring the batteries are charged safely and effectively.
The charging algorithm is responsible for monitoring and controlling the charging current and voltage, which are critical parameters in battery charging. It ensures that the battery is not overcharged, which can lead to damage or even failure, and also prevents undercharging, which can result in insufficient power for the boat's operations. The algorithm adjusts the charging rate dynamically, taking into account factors such as the battery's current state of charge, temperature, and the available power from the charger.
One of the key advantages of using an algorithm in charging is the ability to optimize the charging rate. The algorithm can determine the optimal charging current and voltage levels to maximize the battery's capacity while minimizing charging time. This is particularly important for boat owners who need to ensure their batteries are fully charged for extended periods at sea. By optimizing the charging process, the algorithm helps to extend the battery life and reduce the risk of premature failure.
Additionally, the charging algorithm incorporates safety mechanisms to protect the battery and the boat's electrical system. It can detect and respond to various fault conditions, such as overcurrent, overvoltage, or temperature anomalies. In the event of a fault, the algorithm can initiate a safe shutdown or adjust the charging parameters to prevent damage. This level of control and protection is essential for maintaining the integrity of the boat's electrical system and ensuring the safety of the vessel and its occupants.
Modern boat chargers often feature advanced algorithms that can communicate with the boat's onboard systems. These algorithms can receive data from sensors and other devices, allowing for real-time adjustments to the charging process. For instance, if the boat's engine is running, the algorithm can prioritize charging to ensure the batteries are fully charged for potential extended use. This level of intelligence and adaptability in the charging algorithm contributes to the overall efficiency and reliability of boat power management.
EastEnders Boat Drama: Who Survived the Chaos?
You may want to see also

Safety Features: These include overcurrent protection and temperature monitoring
When it comes to boat charging systems, safety is paramount, especially considering the potential risks associated with electrical systems on boats. This is where the importance of overcurrent protection and temperature monitoring comes into play as crucial safety features.
Overcurrent protection is a critical safety mechanism designed to safeguard the charging system and the boat's electrical network. It operates by monitoring the current flowing through the charging circuit. If the current exceeds a predetermined safe limit, the system triggers an automatic shut-off, preventing potential hazards. This is essential because excessive current can lead to overheating, short circuits, or even fire hazards. For instance, if a faulty appliance or a damaged cable causes a short circuit, the overcurrent protection device will disconnect the power, thus preventing a potential disaster. This feature is often implemented using a circuit breaker or a fuse, which can be manually reset after a safe power-down procedure.
Temperature monitoring is another vital safety feature, especially for lithium-ion batteries commonly used in boat charging systems. These batteries can overheat if not properly managed, leading to potential safety risks. Temperature sensors are strategically placed within the battery pack to monitor its temperature. If the temperature exceeds a safe threshold, the charging system will automatically shut down to prevent overheating and potential damage to the battery. This is particularly important during prolonged charging sessions or in hot environmental conditions. Modern boat charging systems often include temperature-controlled charging algorithms, ensuring that the battery charges at an optimal rate while maintaining a safe temperature.
The combination of overcurrent protection and temperature monitoring ensures that the boat's charging system operates within safe parameters. These features are designed to detect and respond to potential hazards, providing an extra layer of security for both the boat's electrical system and its occupants. It is essential for boat owners and operators to understand these safety mechanisms and regularly inspect their charging systems to ensure they function correctly. By implementing these safety measures, boat charging systems can provide reliable and secure power while minimizing the risks associated with electrical systems on boats.
The Mystery of Kismet Boat's Ownership
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A boat charger, also known as a marine charger, is a device designed to recharge the battery on a boat or any other marine vessel. It works by converting the alternating current (AC) from the boat's power source into direct current (DC), which is suitable for charging the battery. The charger typically has a regulated output voltage and current to ensure the battery is charged efficiently and safely. It monitors the battery's voltage and adjusts the charging rate accordingly, preventing overcharging and potential damage to the battery.
A standard boat charger provides a fixed amount of current to the battery, which may not be optimal for all battery types. Smart chargers, on the other hand, are more advanced and offer several advantages. They can automatically adjust the charging rate based on the battery's condition, using techniques like pulse charging and trickle charging. Smart chargers also provide features like overcharge protection, temperature compensation, and reverse polarity protection, ensuring a safer and more efficient charging process.
While a car charger can provide a basic charging function, it may not be the most efficient or safe option for a boat battery. Car chargers are typically designed for lead-acid batteries and may not have the necessary features to handle other battery types, such as lithium-ion. Additionally, the output voltage and current of a car charger might not match the requirements of a boat battery, potentially leading to overcharging or undercharging. It's best to use a dedicated marine charger for optimal performance and safety.
The charging time for a boat battery depends on various factors, including the battery capacity, the charger's power output, and the initial state of charge. Generally, a deep cycle battery can take several hours to fully charge, while a shallow cycle battery may charge faster. It's important to follow the manufacturer's guidelines and avoid overcharging, as it can reduce the battery's lifespan. Using a smart charger can help optimize the charging process and provide an estimated time remaining until the battery is fully charged.







