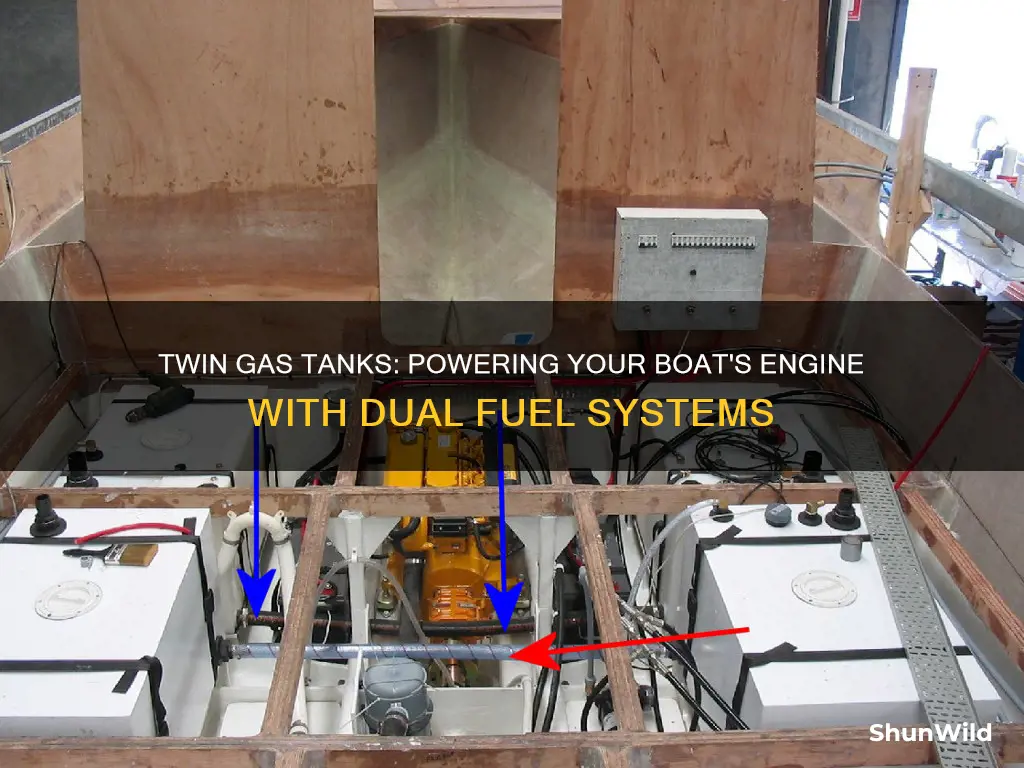
Twin gas tanks on a boat are a crucial component for efficient fuel storage and management. These tanks are designed to hold and supply fuel to the engine, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Understanding how these tanks function is essential for boat owners and operators to maintain their vessels effectively. The system involves a network of pipes, pumps, and valves that distribute fuel from the main tank to the engine, while also incorporating safety measures to prevent overflow and ensure a steady supply. This setup allows for efficient fuel usage and helps maintain the boat's performance and reliability during extended journeys.
What You'll Learn
- Design and Placement: Twin gas tanks are strategically placed for optimal weight distribution and fuel accessibility
- Fuel Injection: Each tank feeds fuel to the engine via individual injectors for precise power delivery
- Fuel Pump: A dedicated fuel pump ensures a consistent flow of fuel from the tanks to the engine
- Ventilation: Gas tanks are vented to prevent vacuum buildup and maintain fuel pressure
- Safety Mechanisms: Overfill protection and pressure relief valves safeguard against fuel tank damage

Design and Placement: Twin gas tanks are strategically placed for optimal weight distribution and fuel accessibility
Twin gas tanks on boats are a crucial component for efficient fuel storage and management, especially in larger vessels. The design and placement of these tanks are carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and safety. The primary goal is to achieve a balanced weight distribution, which is essential for the overall stability and handling of the boat.
In the design phase, engineers and marine specialists take into account various factors. Firstly, the tanks are typically positioned in a way that they are symmetrically placed, often along the centerline of the vessel. This symmetrical arrangement helps to distribute the weight evenly, reducing the risk of capsizing or affecting the boat's trim. By having two tanks, one on each side, the center of gravity remains low, allowing for better maneuverability and control during navigation.
The placement of twin gas tanks also considers accessibility and ease of maintenance. Typically, one tank is positioned forward, closer to the engine compartment, while the other is placed further aft. This arrangement provides easy access to the forward tank, allowing for quick refuelling and maintenance. The aft tank, being more remote, can be used to store larger volumes of fuel, ensuring the boat has an ample supply for extended journeys.
Additionally, the tanks are often designed with a specific orientation to optimize fuel flow. The tanks may be sloped or angled to facilitate the smooth flow of fuel to the engines, especially during acceleration or when the boat is at an incline. This design consideration ensures that the engines receive a consistent fuel supply, promoting efficient combustion and overall engine performance.
Furthermore, the material and construction of the tanks are vital aspects of their design. High-quality, corrosion-resistant materials are used to ensure the longevity and safety of the fuel storage system. The tanks are often made of sturdy materials like steel or specialized composites, capable of withstanding the marine environment and potential impacts. Proper insulation and ventilation are also incorporated to prevent fuel degradation and ensure the safety of the crew and passengers.
Repairing Leaks in Your Porta Boat: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Fuel Injection: Each tank feeds fuel to the engine via individual injectors for precise power delivery
Twin gas tanks on a boat are a common setup to ensure an efficient and reliable fuel supply to the engine. This configuration involves two separate fuel tanks, often located on either side of the vessel, which are designed to work in tandem to power the engine. The primary goal is to provide a consistent and uninterrupted fuel source, allowing the boat to operate smoothly and efficiently.
The system operates by having each tank feed fuel to the engine through individual fuel injectors. These injectors are strategically placed to ensure precise fuel delivery to the engine's combustion chambers. When the engine is running, the fuel injectors spray a measured amount of fuel into the engine's cylinders, where it mixes with air and ignites, creating the power that propels the boat. This process is highly efficient and ensures that the engine receives the exact amount of fuel required for optimal performance.
The use of individual fuel injectors for each tank is a key feature of this design. By having dedicated injectors, the system can precisely control the fuel-air mixture, resulting in improved engine performance and reduced emissions. This level of control is crucial for maintaining the engine's efficiency and longevity, especially during varying load conditions.
In the event of one tank being empty or requiring maintenance, the system is designed to seamlessly switch to the other tank, ensuring the engine continues to run without interruption. This redundancy is a significant advantage, providing peace of mind to boat owners and ensuring that their vessel remains operational even in the event of a fuel tank issue.
Furthermore, twin gas tanks often include additional safety features such as fuel pumps and filters to prevent contamination and ensure a consistent fuel supply. These components work in harmony with the fuel injectors to maintain the engine's performance and reliability, even in demanding marine environments. This setup is a testament to the engineering precision required to power large vessels efficiently and safely.
Treating Sperry Boat Shoes: Pre-Wear Care Tips
You may want to see also

Fuel Pump: A dedicated fuel pump ensures a consistent flow of fuel from the tanks to the engine
A dedicated fuel pump is a crucial component in the system of twin gas tanks on a boat, ensuring a steady and reliable supply of fuel to the engine. This pump is specifically designed to handle the unique requirements of marine fuel systems, providing a consistent flow of fuel from the tanks to the engine, which is essential for optimal performance and efficient operation.
The primary function of the fuel pump is to maintain a constant pressure and flow rate, allowing the engine to receive the required amount of fuel at all times. When the engine is running, the pump creates a vacuum, drawing fuel from the tanks and delivering it to the engine's carburetor or fuel injection system. This process is automatic and continuous, ensuring that the engine always has the necessary fuel for combustion.
In the event of a sudden demand for more power, such as when accelerating rapidly, the fuel pump responds by increasing the pressure and flow rate, providing the engine with the additional fuel required to meet the higher load. This capability is particularly important in high-performance boats or during periods of intense engine usage.
The design and placement of the fuel pump are critical factors in its effectiveness. It is typically located close to the engine to minimize the distance fuel must travel, ensuring a quick response to engine demands. Additionally, the pump's capacity and power output are carefully chosen to match the boat's fuel requirements, preventing issues like fuel starvation or excessive pressure that could lead to engine damage.
Regular maintenance and inspection of the fuel pump are essential to ensure its longevity and optimal performance. This includes checking for any signs of wear, debris, or contamination that could affect the pump's efficiency. By keeping the fuel pump in good condition, boat owners can ensure that their twin gas tank system operates smoothly and reliably, providing a seamless and enjoyable boating experience.
Stripping Paint from an Aluminum Boat: Effective Methods
You may want to see also

Ventilation: Gas tanks are vented to prevent vacuum buildup and maintain fuel pressure
Ventilation is a critical aspect of the design and operation of twin gas tanks on boats, ensuring optimal performance and safety. The primary purpose of ventilation is to prevent the formation of a vacuum within the fuel tanks, which could lead to a decrease in fuel pressure and potential engine issues. When a boat is stationary or moving at low speeds, the fuel in the tanks can experience a drop in pressure due to the lack of constant flow and agitation. This vacuum buildup can cause several problems.
To address this, gas tanks are equipped with vents, typically located at the top of the tank, just above the fuel level. These vents serve as a pathway for air to enter the tank, replacing the fuel that has been used and preventing the formation of a vacuum. As the boat's engine operates, it creates a constant flow of air through the vent, ensuring that the fuel level remains stable and the pressure is maintained. This is especially important during extended periods of idling or when the boat is stationary for an extended duration.
The design of the vents is crucial to their effectiveness. They are often designed with a small opening to allow for controlled air intake, preventing excessive air from entering the tank, which could lead to fuel evaporation and potential engine issues. The vents are also typically equipped with filters to trap contaminants and ensure that only clean air enters the fuel system. This filtration process is essential to maintaining the quality of the fuel and preventing engine damage.
In addition to preventing vacuum buildup, ventilation also plays a role in fuel stability. By allowing air to circulate within the tank, the vents help to dissipate volatile compounds and maintain the fuel's chemical stability. This is particularly important for boats that operate in varying weather conditions, as it ensures that the fuel remains usable and does not degrade over time. Proper ventilation also contributes to the overall longevity of the fuel system, reducing the risk of fuel-related problems and the need for frequent maintenance.
In summary, ventilation in twin gas tanks is a vital feature that ensures the efficient and safe operation of a boat's fuel system. By preventing vacuum buildup and maintaining fuel pressure, the vents allow for optimal engine performance and stability. The design and placement of vents, along with their filtration capabilities, contribute to the overall reliability and longevity of the boat's fuel supply, making it a critical component of any marine vessel's design.
Simple Machines: Paddle Boat Wheel Explained
You may want to see also

Safety Mechanisms: Overfill protection and pressure relief valves safeguard against fuel tank damage
The twin gas tanks on a boat are a crucial component for fuel storage and supply. These tanks are designed to provide a reliable and efficient fuel system, ensuring the boat's engine(s) have an adequate supply of fuel during extended periods of use. One of the key aspects of this design is the integration of safety mechanisms that protect the fuel tanks from potential damage, ensuring the boat's safety and longevity.
Overfill protection is a critical safety feature in twin gas tank systems. When a fuel tank is filled, the system is designed to prevent the tank from being overfilled, which could lead to fuel spillage, damage to the tank, and potential hazards. This protection is typically achieved through a sensor or a mechanical float switch. The sensor monitors the fuel level and triggers an alarm or a warning signal if the tank is about to reach its maximum capacity. This early warning system allows the operator to stop the fueling process before the tank is overfilled, thus preventing any potential issues.
In addition to overfill protection, pressure relief valves are another essential safety mechanism in twin gas tank systems. These valves are designed to release excess pressure that may build up within the fuel tanks. Fuel, especially when it's in a liquid state, can expand when heated and contract when cooled. This expansion and contraction can create pressure within the tank. If this pressure is not managed, it can lead to fuel tank damage, leaks, and potential safety hazards. Pressure relief valves are strategically placed to allow the release of this excess pressure, ensuring that the fuel tanks remain intact and functional.
The pressure relief valves are typically designed to open at a specific pressure threshold, which is determined by the manufacturer. When the pressure inside the tank exceeds this threshold, the valve opens, allowing the excess pressure to be released into the atmosphere or into a designated vent system. This process helps to maintain the structural integrity of the fuel tanks and prevents any potential damage that could compromise the boat's safety.
By incorporating overfill protection and pressure relief valves, the twin gas tank system on a boat is designed to provide a safe and efficient fuel storage solution. These safety mechanisms are crucial in preventing fuel tank damage, ensuring the boat's stability, and maintaining the overall safety of the vessel and its occupants. Understanding and maintaining these safety features are essential for any boat owner to ensure a reliable and secure boating experience.
The Perfect Power Boat: Features and Factors
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Twin gas tanks, also known as twin fuel tanks, are a common feature in marine engines and serve as a safety measure to ensure a consistent fuel supply. These tanks are designed to store fuel, typically gasoline or diesel, and are often used in conjunction with a single engine or multiple engines, depending on the boat's size and power requirements.
Twin gas tanks provide several advantages. Firstly, they offer redundancy, meaning if one tank is affected by a leak or contamination, the other tank can still supply fuel to the engine(s). This setup helps prevent engine starvation and ensures the boat can continue operating even if one tank is compromised. Additionally, twin tanks allow for better fuel management by providing separate compartments, which can be useful for separating different types of fuel or for storage during long voyages.
Yes, maintenance is an important aspect of owning a boat with twin gas tanks. Regular inspections are crucial to identify any potential issues. This includes checking for leaks, ensuring the tanks are properly vented, and maintaining the fuel filters to prevent contamination. It is also recommended to use the correct fuel stabilizers and additives to maintain the fuel's quality, especially in twin tank systems where fuel can be stored for extended periods. Proper maintenance will help ensure the longevity and reliability of the boat's fuel system.







