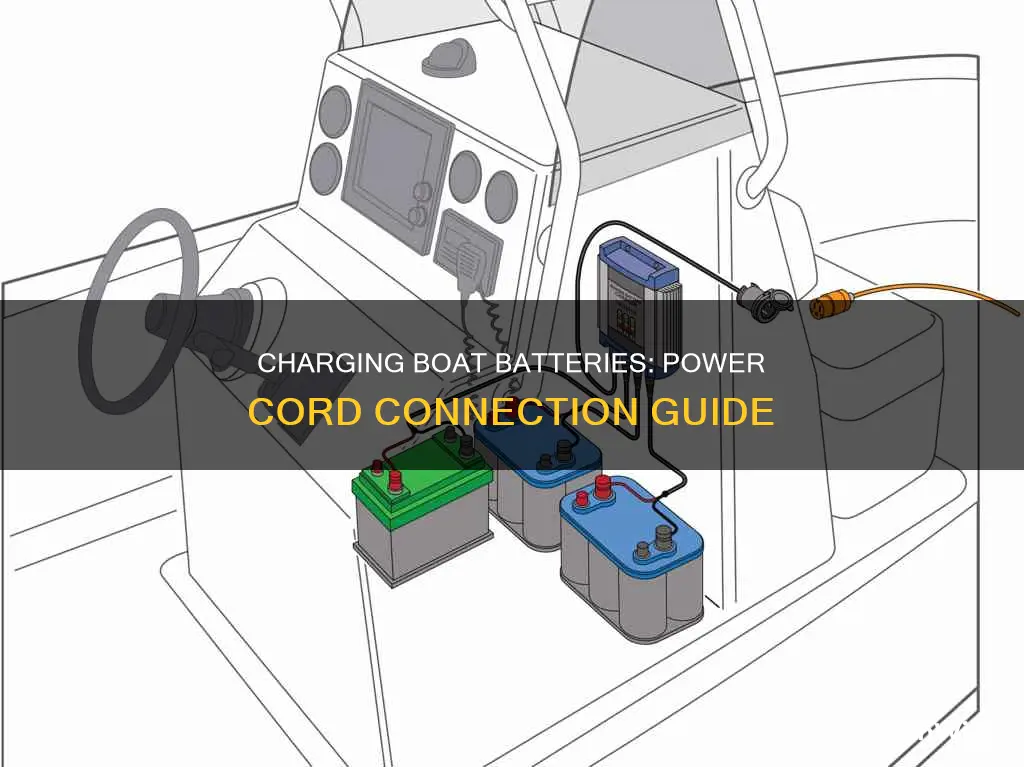
Charging a boat battery from a power cord is a relatively simple process, but it's important to know what type of battery you have and to choose the right charger. Most boats are equipped with deep-cycle batteries, which can be drained and recharged multiple times. The first step is to select a charger that matches your battery's chemistry and voltage. There are two main types of chargers: onboard and portable. Onboard chargers are already connected to the battery system, while portable chargers can be used anywhere and are less expensive. Once you've chosen the right charger, simply connect the red (positive) cable to the red terminal and the black (negative) cable to the black terminal. Then, plug in the charger and turn it on. When the battery is fully charged, be sure to disconnect the charger and unplug it before starting the engine.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Types of marine battery chargers | Onboard and portable |
| Onboard marine chargers | Permanently installed on the boat and connected directly to the boat's electrical system |
| Onboard marine chargers advantages | Automatic charging as they continuously monitor the battery's condition and adjust the charging rate accordingly |
| Onboard marine chargers disadvantages | Requires carrying and connecting a portable charger each time |
| Portable marine chargers | Compact and versatile, designed to be carried on board or used on land to charge batteries when docked |
| Portable marine chargers advantages | Flexibility and mobility, especially when far from shore power or marinas |
| Portable marine chargers disadvantages | Need to be monitored while charging to prevent overcharging |
| Charger compatibility | The charger must match the voltage of the battery |
| Charger amperage output | Should be around 10-20% of the battery's capacity |
| Charging lead-acid batteries with shore power | Takes up to 10 hours to charge and need to be fully charged to avoid damage |
| Charging lithium batteries with shore power | Takes significantly less time and will not be damaged if not fully charged |
What You'll Learn
- Shore power: the electrical plug-ins at boat slips, providing electricity via AC power
- Onboard chargers: permanently installed, they charge multiple batteries at once
- Portable chargers: versatile and compact, they are ideal for charging on water
- Battery compatibility: ensure the voltage and amperage of the charger match the battery
- Charging lead-acid batteries: these take longer to charge and require regular maintenance

Shore power: the electrical plug-ins at boat slips, providing electricity via AC power
Shore power is a crucial aspect of marine battery charging, providing a reliable electricity source for boats docked at marinas or harbours. It involves utilising electrical plug-ins, known as shore power outlets or power pedestals, located at boat slips to deliver AC (alternating current) power to vessels. This power source offers numerous benefits for boat owners, especially when it comes to charging batteries and operating various appliances.
Understanding Shore Power
Shore power is the electrical supply provided to boats, ships, or other vehicles when they are docked, moored, or berthed. This power comes from the electrical grid, delivering AC power that is easily accessible for various applications. The term shore power emphasises the distinction between power sources available on shore and those used offshore or at sea.
Electrical Plug-ins at Boat Slips
At boat slips, marinas, or harbours, you'll find dedicated electrical plug-ins designed to provide shore power. These outlets are often part of a power pedestal or tower, featuring a 30-amp connection with two female receptacles and a protective hinged lid. It's important to ensure the amperage of your boat's electrical system matches the shore power outlet, and if not, use appropriate adapters.
Providing Electricity via AC Power
Shore power delivers AC power, which differs from the DC (direct current) power stored in batteries. AC power is versatile and can be easily converted to high voltages, making it suitable for long-distance transmission over the electrical grid. This type of power is used by most appliances and electrical devices, such as TVs, microwaves, hair dryers, power tools, and more. By plugging into shore power, boat owners can directly utilise this AC power for their devices without relying on battery power or inverters.
Charging Boat Batteries
One of the primary uses of shore power is charging boat batteries. While docked, boat owners can use shore power to recharge their batteries efficiently. This process typically involves having the right charge controller or battery charger, specifically designed for marine use. Shore power provides a convenient and reliable way to ensure batteries are charged and ready for the next excursion.
Benefits of Shore Power
Shore power offers several advantages for boat owners. Firstly, it eliminates the need for generators or other power sources, reducing fuel consumption and associated air pollution. Secondly, it provides a consistent power source for appliances and devices, enhancing the comfort and convenience of life on board. Additionally, shore power contributes to the maintenance of engines and generators, reducing noise and facilitating a more peaceful environment.
In summary, shore power, with its electrical plug-ins at boat slips, plays a vital role in providing electricity via AC power to boats and ships. It offers a safe, efficient, and environmentally friendly way to charge batteries and power various devices, making it an essential aspect of modern boating and maritime operations.
Launching a Boat: Mastering the Manual Transmission
You may want to see also

Onboard chargers: permanently installed, they charge multiple batteries at once
Onboard chargers are permanently installed on your boat and are a convenient way to ensure your batteries are always charged and ready to go. They are designed to handle the marine environment, offering protection against water, vibration, and corrosion. These chargers work by converting AC power from your boat's electrical system into DC power that is used to charge your batteries.
Onboard chargers are made up of separate battery chargers (known as "banks") housed together in a single casing that can be mounted on your boat. This allows you to charge multiple batteries at the same time. They are typically more technologically advanced than portable chargers and feature multi-stage charging, which can help extend battery life and improve performance.
When selecting an onboard charger, it is important to consider the type and number of batteries your boat has, as well as the charger's capacity and features. Choose a charger that matches the voltage of your boat's battery system—most boats use 12-volt systems, but some may have 24-volt or 36-volt configurations. Additionally, check the charger's amperage rating to ensure it is compatible with your battery's specifications.
The installation process for an onboard charger is relatively simple and can be completed in a few hours. First, select a mounting area that stays dry and allows for space in front and on each side of the charger. Ensure the mounting surface can support the weight of the charger, and that the DC and AC cords will be able to reach their respective connections. Use the supplied template to mark and drill the mounting holes, then attach the charger using the provided screws and marine sealant.
Next, route and attach the DC leads to the battery posts, ensuring each post is free of corrosion and that the polarity is correct. If the DC leads are too short, you may need to purchase extensions. Route the AC power cord to a place that is easily accessible when you need to connect to a power source, but can also be tucked away in a dry location when you are out on the water.
Finally, connect the charger to a power source and test it. Observe the charger's indicator lights to ensure it is functioning correctly, and check the voltage of the batteries using a multimeter to confirm they are receiving a charge.
Boat Owner's Official Job Title: Captain or Something Else?
You may want to see also

Portable chargers: versatile and compact, they are ideal for charging on water
Portable chargers are compact and versatile, making them an ideal solution for boat battery charging on water. They are designed to be carried on board or used onshore when docked, offering flexibility and convenience. Here are some key advantages of portable chargers:
Compatibility with Various Boat Types
Portable chargers are suitable for smaller boats like dinghies, kayaks, small fishing boats, and personal watercraft. They are also ideal for boats where installing a fixed-mount charger is impractical or impossible. This versatility ensures that a wide range of boat owners can benefit from the convenience of portable charging solutions.
Variety of Models
Portable marine chargers come in a range of models, including manual, automatic, and smart chargers. Smart chargers, in particular, are an excellent choice due to their advanced technology. They employ a multi-stage charging approach, optimising the charging process and prolonging battery life. This makes them a wise investment for any boat owner concerned about maintaining healthy marine batteries.
Cost-Effectiveness
Portable chargers are generally more cost-effective than installing onboard charging systems. This makes them a popular choice among budget-conscious boaters. With a portable charger, you can avoid the expense of a permanent installation while still enjoying reliable charging capabilities.
Adaptability to Diverse Charging Needs
Portable chargers can be used with multiple boats, making them perfect for boat owners with diverse charging needs or those who frequently use rental boats. Their adaptability ensures that you can carry a single charger that can be used across various vessels, eliminating the hassle of managing multiple chargers.
Ease of Use
Portable chargers are straightforward to use and can be easily connected to your boat's battery when needed. This convenience is especially valuable for boat owners who want a simple and efficient charging solution without the complexity of permanent installations.
In summary, portable chargers offer versatility, compactness, and adaptability, making them a preferred choice for boat battery charging on water. They are designed to meet the diverse needs of boat owners, providing reliable and flexible charging solutions.
The Boat Trip: Miami to Nassau Distance Explored
You may want to see also

Battery compatibility: ensure the voltage and amperage of the charger match the battery
When charging a boat battery, it is crucial to ensure that the voltage and amperage of the charger match the battery. This compatibility is essential for the charging process to be safe and effective. Here are some detailed instructions to guide you through this process:
First, identify the voltage of your boat battery. Most marine batteries operate at 12 volts, but some boats may use 24-volt or 36-volt batteries. The voltage of your battery should be indicated on the battery itself. It is important to select a charger that matches this voltage. Using a charger with the wrong voltage can be unsafe and may damage your battery.
Next, consider the battery's capacity, which is measured in ampere-hours (Ah). The amperage output of the charger should typically be around 10-20% of the battery's capacity. For example, if you have a 100Ah battery, a suitable charger would be one with an output of 10-20 amps. This calculation ensures that the charger can effectively charge your battery without overwhelming it.
When dealing with multiple batteries, the charging process becomes more complex. The configuration of your batteries, whether connected in series or parallel, will determine the charger requirements. If your batteries are connected in series, their voltages add up. So, if you have two 12-volt batteries in series, you'll need a 24-volt charger. On the other hand, if your batteries are connected in parallel, the voltage remains the same, but the capacity (amp-hours) increases. In this case, your charger should be able to handle the combined amperage needs of the parallel-connected batteries.
Additionally, consider the type of battery you have. Deep cycle batteries, for instance, should not be jump-started. Instead, they need to be charged using a dedicated charger. Different types of batteries may have specific charging requirements, so it's important to refer to the manufacturer's instructions for your particular battery type.
Finally, when selecting an onboard charger, choose one that is fully waterproof, resistant to corrosion, and suitable for mounting in damp or wet locations. This is especially important for boats, as the marine environment can be harsh and corrosive.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your boat battery charger is compatible with your battery in terms of voltage and amperage, making the charging process safe and efficient.
The Northwestern Boat's Fate on Deadliest Catch
You may want to see also

Charging lead-acid batteries: these take longer to charge and require regular maintenance
Charging lead-acid batteries can be a time-consuming and labour-intensive process. They generally have a runtime of 5 to 6 hours and take around 8 hours to recharge. However, the process doesn't end there. After charging, lead-acid batteries require a cooldown period of another 8 hours, bringing the total time needed for the battery to be operational again to 16 hours. This lengthy process can impact day-to-day operations and scheduling.
To charge a lead-acid battery, trained personnel must first use lifting equipment to remove the battery and place it on a storage rack. The battery's weight makes this step necessary. Once the battery is charged, it must be left to cool down for an additional 8 hours. During this time, the battery may be moved to a designated cooling area if the space is needed for other batteries. After the cooldown period, it is important to check the electrolyte levels and refill the battery with distilled or deionized water to prevent the chemical process from degrading and causing early battery failure.
The drawbacks of lead-acid batteries have led to a growing preference for lithium-ion batteries, which offer faster charging times of around 1 to 2 hours and do not require a cooldown period. This allows for "opportunity charging" during breaks or between shifts. Additionally, lithium-ion batteries can remain in the equipment while charging and do not need to be refilled with water, saving space and labour time.
When charging lead-acid batteries, it is crucial to avoid overcharging, as this can damage the battery and reduce its lifespan. Lead-acid batteries are made from toxic lead and sulfuric acid, and overcharging can cause the electrolyte solution to overheat, leading to gas formation and increased pressure inside the battery. While the battery is designed to relieve pressure, it may not always function properly, resulting in a potential explosion. Therefore, it is essential to monitor battery conditions and adjust the charging process to prevent overcharging.
To maintain the health of lead-acid batteries, it is recommended to keep them fully charged whenever possible. Lead-acid batteries are prone to sulfation, which occurs when the battery remains partially charged for extended periods. Regular maintenance is also important, including checking the state of charge, electrolyte levels, and the condition of terminal connections. Clean the terminals if they are corroded and ensure they are tight. If the boat is not in use for an extended period, consider using a battery maintainer or trickle charger to keep the battery in good condition, and always store batteries in a cool, dry place.
Bass Boat Restoration: Reviving the Finish for a Fresh Look
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Shore power refers to the electrical plug-ins at boat slips that provide electricity. To charge your boat battery using shore power, you'll need to have the right charge controller. This can be a standard converter charger or an inverter charger. Ensure that the amperage of your electrical system matches the amps from the shore power outlet. If not, use the right adapters.
Onboard chargers are permanently installed on the boat and connected directly to the boat's electrical system. They offer automatic charging and monitor the battery's condition. Portable chargers, on the other hand, are versatile and can be used anytime, anywhere. They are less expensive and more suitable if you are frequently far from shore power.
Match your charger to your boat battery's chemistry and voltage. Ensure that the charger is compatible with the type of battery you have, whether it's a lead-acid or lithium-ion battery. Also, consider the battery's capacity, measured in ampere-hours (Ah), and choose a charger with an output of about 10-20% of the battery's capacity.
First, connect the red (positive) cable to the red terminal, and then connect the black (negative) cable to the black terminal. Plug in the charger and turn it on. If you're using a smart charger, it will stop charging automatically. Otherwise, you'll need to set a timer and manually disconnect it once it's finished.
To disconnect the charger, first, unplug it from the power source. Then, remove the black cable from its terminal, followed by the red cable. Ensure you always disconnect in the reverse order of connection.







